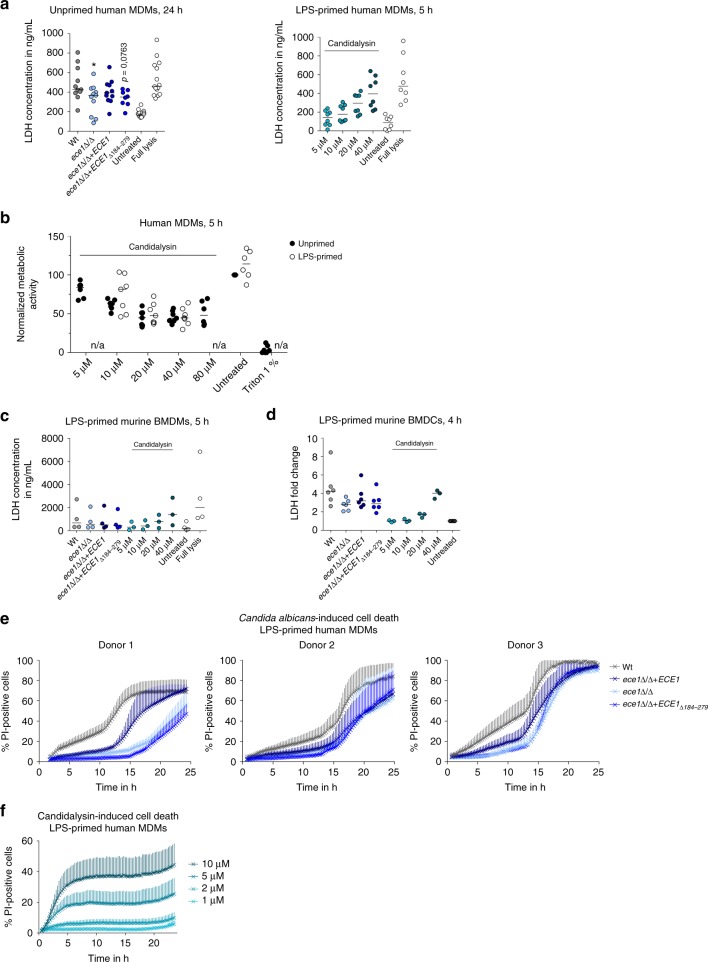
Fig. 8.
Candidalysin-dependent damage of hMDMs. a, c, d Macrophage lysis was quantified by measuring LDH release in a unprimed hMDMs or LPS-primed c mBMDMs or d mBMDCs that were infected with C. albicans Wt, re-integrant (ece1Δ/Δ + ECE1) or mutant strains (ece1Δ/Δ, ece1Δ/Δ + ECE1Δ184–279) (MOI 6) for 5 or 24 h and in LPS-primed a hMDMs, c mBMDMs, or d mBMDCs that were incubated with synthetic Candidalysin for 5 h. b Metabolic activity of LPS-primed or unprimed hMDMs treated with synthetic Candidalysin for 5 h was measured using XTT. 1% Triton X-100 was added as a positive control. e, f Macrophage damage over time was assessed by quantifying propidium iodide (PI)-positive cells in LPS-primed hMDMs infected with e C. albicans Wt, re-integrant (ece1Δ/Δ + ECE1) or mutant strains (ece1Δ/Δ, ece1Δ/Δ + ECE1Δ184–279) (MOI 6) or f incubated with synthetic Candidalysin. a–d Values are represented as scatterplot with median of at least three different donors (n ≥ 3). For statistical analysis, a one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparison test was used. *p ≤ 0.05, significance compared to Wt infection. e The results of three different donors are displayed separately due to strong donor variability. Data are shown as mean + SD of two independent positions in two wells. f Data are shown as mean + SD of six independent donors