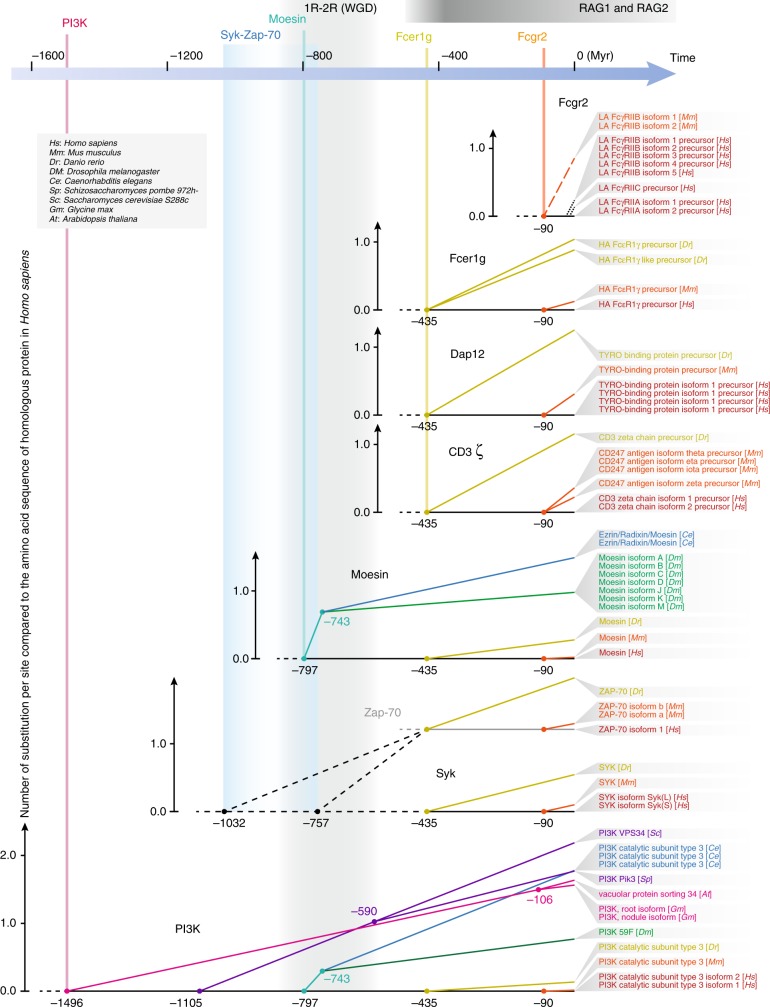
Fig. 7.
Potential evolutionary implications of PIP2-based signaling in modern immune receptor-based phagocytosis. Phylogenetic trees of Fc γ receptor II family proteins (Fcgr2), Fc ε receptor γ subunit (Fcer1g), DAP12 (Tyrobp), CD3 ζ chain, Moesin, Syk family proteins (ZAP70 and Syk), and PI3 kinase catalytic subunit (PI3K) are shown. On top of the figure, the time axis is shown in the unit of million years. For each tree, the time axis is shown on the bottom, and is aligned to the time axis on the top. The species divergence times from published studies are used. For each tree, the vertical axis on the left shows the number of substitution per site compared to the amino acid sequence of the homolog in Homo sapiens, so the slope of each branch represents amino acid substitution rate. The gray column indicates the time interval of two rounds of whole-genome duplication (WGD) during the evolution of common ancestors of chordates (1R) and vertebrates (2R). The dark gray bar on top of the figure indicates the time interval of emergence of RAG1 and RAG2 (not the RAG invasion itself)