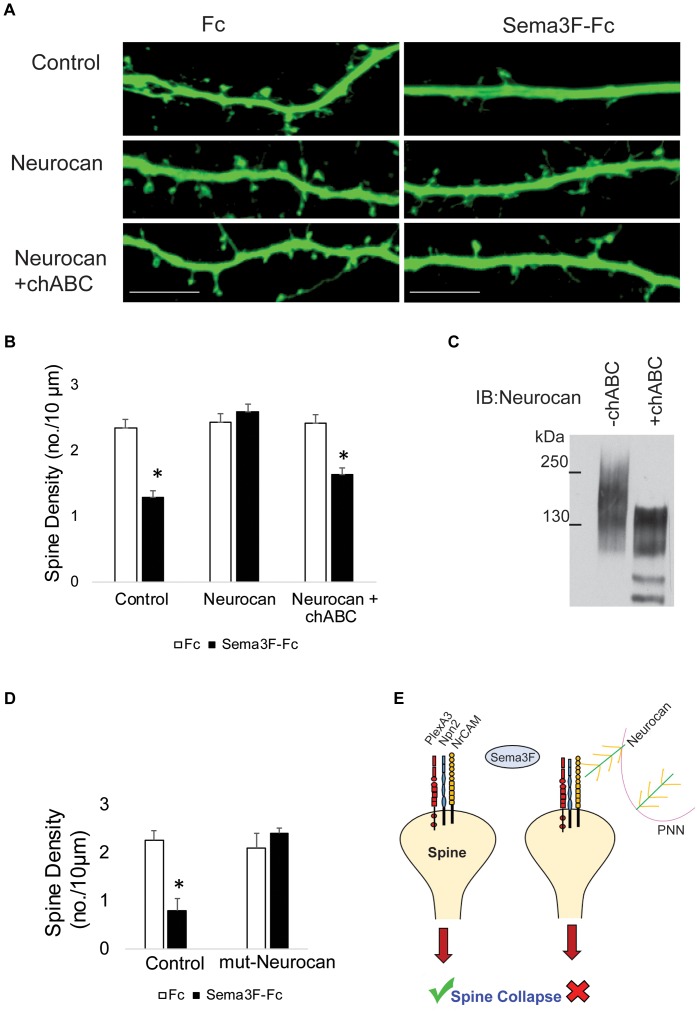
FIGURE 5.
Enzymatic digestion of Neurocan GAG chains with chondroitinase ABC decreases its ability to inhibit Sema3F-induced spine retraction. (A) Images showing spines on apical dendrites from cortical neurons (EGFP, green) in culture treated with Fc or Sema3F-Fc. Neurocan blocked Sema3F-mediated spine retraction, whereas chABC-treated Neurocan was not effective. Scale bar = 10 μm. (B) Quantification of experiment in panel A shows a significant reduction in mean spine density of control neurons treated with Sema3F-Fc compared to Fc. Sema3F-induced spine retraction was fully blocked by 20 nM Neurocan, as well as by chABC-digested Neurocan (∗p < 0.05, t-test; n = 3, 10 neurons per condition). (C) Immunoblotting of Neurocan before and after treatment with chABC to remove GAG chains. A shift in apparent molecular size of chABC-treated Neurocan was observed, reflecting a decrease in GAG content. (D) Mouse cortical neurons with and without pre-treatment with recombinant mutNeurocan lacking the C-terminal sushi domain (20 nM, 30 min) showed the mouse Neurocan fragment inhibited Sema3F-Fc induced spine retraction. (E) Model showing that interaction of the PNN protein Neurocan with NrCAM on the surface of dendritic spines in cortical pyramidal neurons terminates Sema3F-induced dendritic spine remodeling during postnatal maturation. Neurocan core protein is depicted in green with yellow GAG chains. The Sema3F receptor complex is composed of NrCAM (yellow), Npn2 (blue), and PlexA3 (red) subunits.