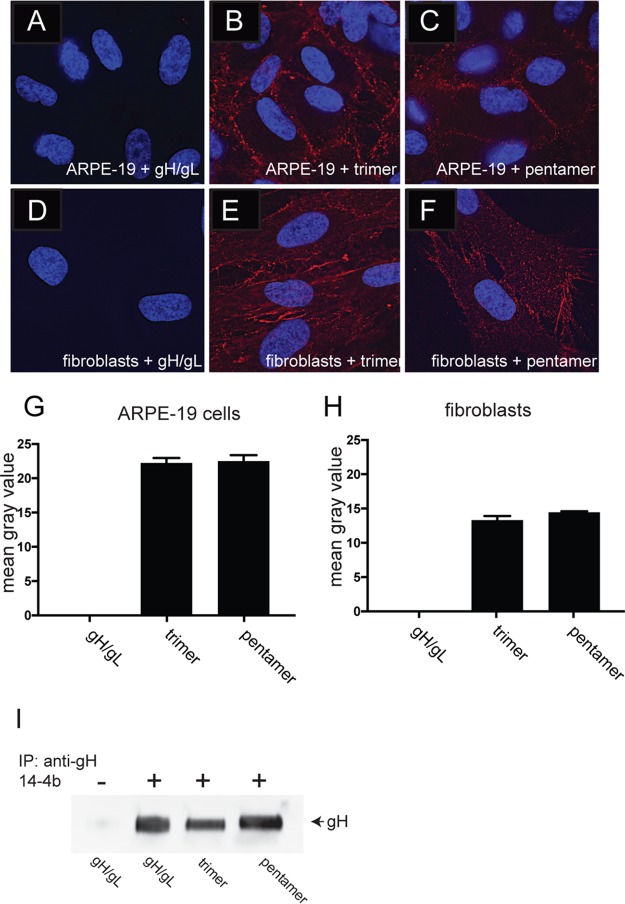
FIG 3.
Binding of soluble protein complexes to cell surfaces. ARPE-19 cells (A to C) or fibroblast cells (D to F) seeded on glass coverslips were incubated with different soluble protein complexes (100 μg/ml) for 1 h at 4°C. The cells were then washed once in cold PBS and then fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde and processed for immunofluorescence microscopy. Protein complexes were detected using anti-gH MAb 14-4b followed by Dylight-594 goat anti-mouse secondary antibody. The cells were then permeabilized, counterstained with DAPI (4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole), and then mounted onto glass slides with Fluoromount-G. Images were captured by a 60× objective with the Deltavision Core DV Widefield Deconvolution system. (G and H) Histograms showing the quantification of soluble protein binding to cell surfaces for conditions represented in panels A to C (G) and D to F (H). The data are displayed as mean gray values (arbitrary units) as analyzed by ImageJ. Data were collected from three separate images for each condition. (I) Immunoprecipitation of soluble gH/gL protein complexes followed by Western blot analysis. The top of the panel indicates whether the conformational specific anti-gH MAb 14-4b was included (plus) or omitted (minus) in the immunoprecipitation, and the bottom of the panel indicates which protein complex was used for the immunoprecipitation. The membrane was probed with MAb AP-86, which is specific for the gH polypeptide.