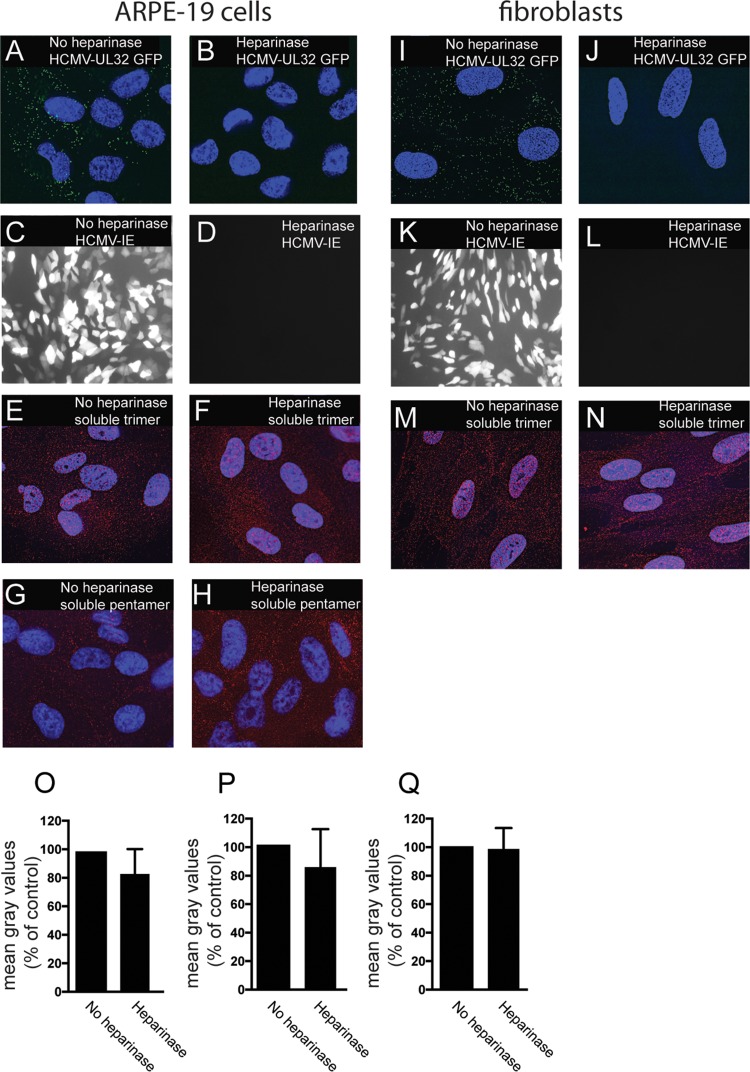
FIG 5.
Binding of soluble proteins to cell surfaces is not affected by heparinase treatment. ARPE-19 or fibroblast cells seeded on glass coverslips were incubated in buffered Opti-MEM at 30°C and either left untreated (no heparinase) or treated with heparinase enzyme and incubated at 30°C for 2 h. The cells were then subjected to one of the following conditions. For panels A, B, I, and J, ARPE-19 (A, B) and fibroblast (I, J) cells were incubated with HCMV TB40E-UL32-GFP virus particles at 4°C for 1 h and then fixed and analyzed by deconvolution microscopy as described for Fig. 4. For panels C, D, K, and L, ARPE-19 (C, D) or fibroblast (K, L) cells were incubated with HCMV BADrUL131 for 2 h and then washed and allowed to incubate for an additional 24 h, at which time the cells were fixed and analyzed by immunofluorescence microscopy to detect the HCMV GFP expression. For panels E, F, M, and N, cells were incubated with soluble trimer complexes (100 μg/ml). For panels G and H, cells were incubated with soluble pentamer complexes (100 μg/ml) at 4°C for 1 h. The cells were then washed once in cold PBS and then fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde and processed for immunofluorescence microscopy using anti-gH MAb 14-4b as described for Fig. 3. (O to Q) Histograms showing the quantification of HCMV virus particles binding to cell surfaces for the conditions represented in panels E and F, G and H, and M and N, respectively. The data are displayed as mean gray values (arbitrary units) relative to control conditions as analyzed by ImageJ. Data were collected from three separate images for each condition.