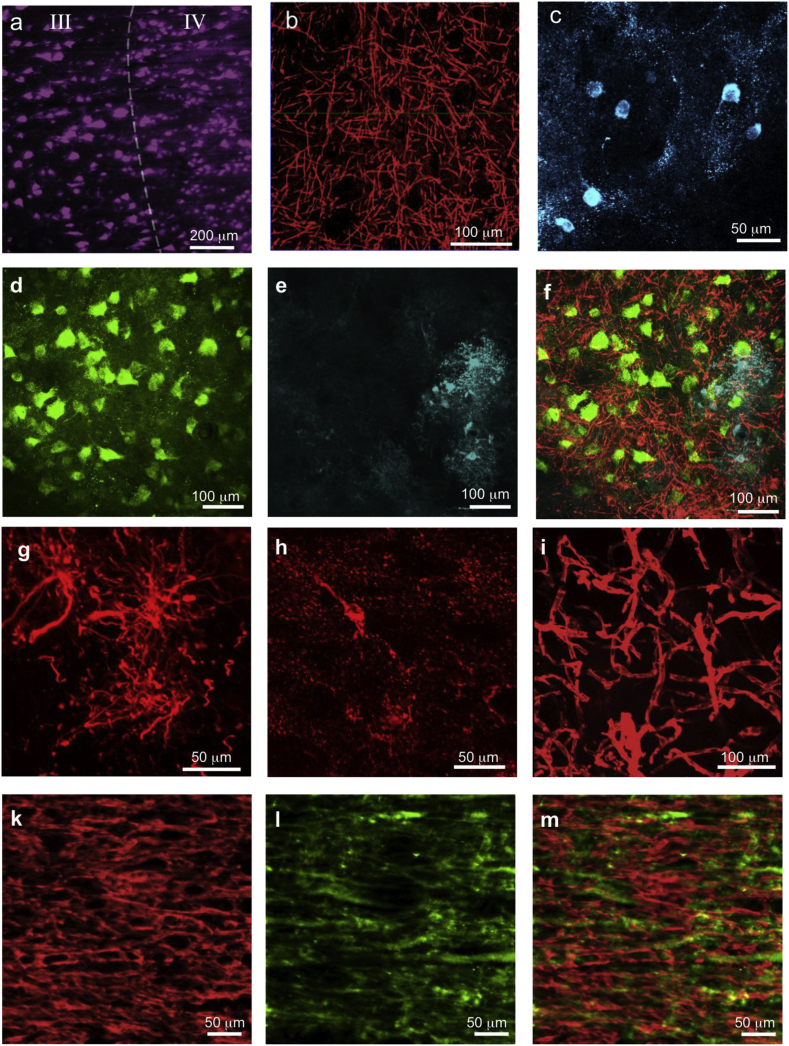
Fig. 2.
Immunohistochemical staining of human post mortem brain tissue after clearing. High contrast of all stains reveals preserved protein composition of the sample despite lipid loss upon intensive clearing. (a) Cortex subsample (1 A) with 3 mm × 3 mm x 5 mm size stained with neuron marker HuC/D. Cortical layers III and IV can be identified based on neuronal morphology. See Video S1 for 3D version of entire imaging volume; (b) Myelinated fibers in the cortex subsample (1 B) stained for protein component MBP (myelin basic protein, 3 mm × 3 mm x 3 mm sample size). See Video S2 for 3D version of entire imaging volume; (c) Subsample (1C) stained for parvalbumin, a calcium binding protein for sub-classification of neurons, especially to identify fast spiking interneurons; (d–f) Cortex subsample (1D) triple stained for neurons ((d), HuC/D, green), astrocytes ((e), GFAP, cyan) and myelinated fibers (MBP, red); (f) overlay; (g) Cortex subsample (1E) stained for astrocytes (GFAP, red); (h) Cortex subsample (1F) stained for microglia (Iba-1, red); (i) Vessels in the cortex subsample (1G) stained with helix aspersa agglutinin; (k,l,m) Double labeling of corpus callosum subsample (3 A) stained for (k) MBP and (l) β-III-tubulin; (m) overlay of both stains. Imaging of corpus callosum (k, l, m) was performed in PBS (all other samples were TDE embedded), thus tissue is 1.25 times expanded as compared to its original size. Image (a) is acquired with light-sheet microscope, images (b–m) are acquired using laser scanning microscope.