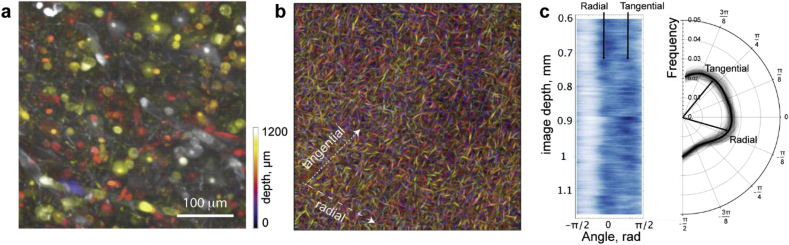
Fig. 7.
Classification algorithm enhances linear structures and allows studying fiber orientation distribution within a volume similar to an MRI voxel volume. (a) Original data (subsample 1H) projected by a color-coded maximum intensity projection (color represents imaging depth, see scale). (b) The processed stack (after classification and vesselness filtering) shown in the same projection as in (a). Orientation of fiber structures in the image volume: (c) Fiber orientation distribution. Heat map shows the directionality (in-plane) distribution at each slice along the depth of a 600 × 600 × 600 μm3 volume at an imaging depth of 600 μm. Slices are running at the constant cortical depth. Circular histogram showing the distribution of fibre directionality averaged over the entire 600 μm range. Major fibre directions (corresponding to radial and tangential fiber orientations with respect to cortical) are indicated by arrows in (b).