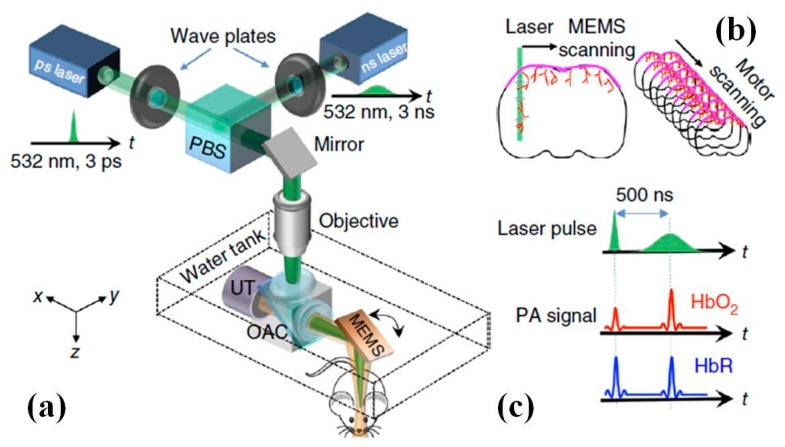
Figure 19.
MEMS based fast functional photoacoustic microscopy (PAM) of the mouse brain. (a) Schematic drawing of the PAM system. OAC, optical-acoustic combiner; PBS, polarizing beam splitter; UT, ultrasonic transducer. (b) Scheme of PAM scanning. 3D imaging is achieved by fast MEMS mirror scanning along the x-axis and slow motor-stage scanning along the y-axis. (c) Sequence of PAM excitation and detection. The picosecond pulse incident on oxyhemoglobin (HbO2) results in more saturation and thus a weaker photoacoustic amplitude (PA) signal than the following nanosecond pulse, whereas the difference for deoxyhemoglobin (HbR) is negligible (Reproduced with permission from Nature Publisher Group [112]).