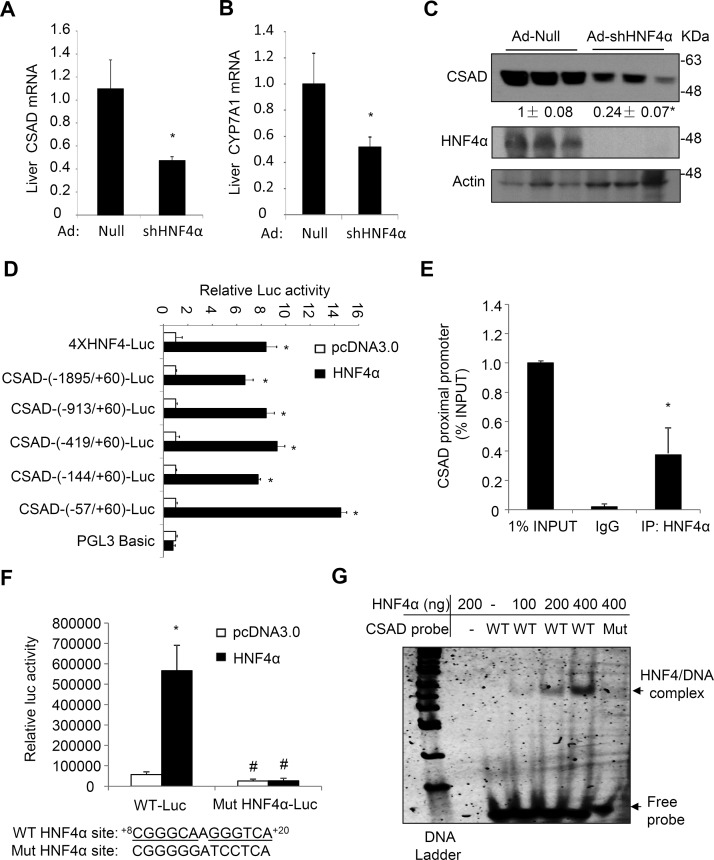
Figure 3.
Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α (HNF4α) binds mouse CSAD promoter to induce its gene transcription. (A–C) C57BL/6J male mice (n = 5) were injected with Ad-Null or Ad-shHNF4α at a dose of 1 × 109 pfu/mouse. After 7 days, mice were fasted overnight, and tissues were collected. Liver mRNA and protein were measured. The mRNA results are expressed as mean ± SEM. *Statistical significance versus Ad-Null. Densitometry was performed using ImageJ software and normalized to loading controls. (D) Luciferase reporter constructs (0.2 μg), β-gal expression construct (0.05 μg), and 0.1 μg of pcDNA3.0 or HNF4α expression plasmid were cotransfected into AML12 cells. Luciferase and β-gal activities were measured 48 h later. Controls (pcDNA3.0) for different reporter constructs were normalized to “1” for comparison. *Statistical significance versus pcDNA3.0. The indicated promoter length is relative to the transcriptional start site of the Csad gene as “+1”. The “ATG” start codon of the Csad gene starts at +169 bp. (E) Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay detection of HNF4α occupancy to the proximal promoter region of the Csad chromatin in mouse livers. The ChIP assay real-time PCR primer pairs amplify the −57/+60 Csad chromatin region. (F) Wild-type (WT) and HNF4α mutant CSAD-(−913/+60)-luc constructs (0.2 μg), β-gal expression construct (0.05 μg), and 0.1 μg of pcDNA3.0 or HNF4α expression plasmid were cotransfected into AML12 cells. Luciferase and β-gal activities were measured 48 h later. The putative HNF4α binding site and mutant sequences are shown below the bar graph. *Statistical significance versus pcDNA3.0. #Statistical significance versus WT-Luc. (G) EMSA detection of HNF4α binding to the WT but not the mutant HNF4α binding site in the CSAD promoter DNA probe. Mut, CSAD probe with mutations introduced into the HNF4α binding site as shown in (C). All reporter assay results are shown as mean ± SD of triplicate assays.