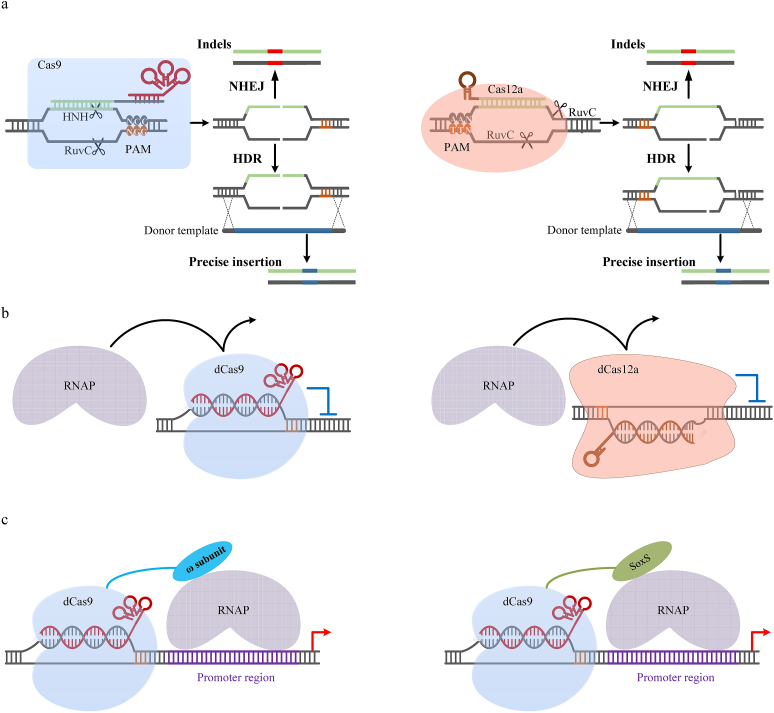
Fig. 3.
CRISPR genome editing (a) and CRISPR gene regulation including CRISPR interference (b, CRISPRi) and CRISPR activation (c, CRISPRa). The genome editing starts from the introduction of DSBs (double-stranded breaks) followed by NHEJ and HDR DNA repair. CRISPRi uses dCas (dCas9 or dCas12a) to sterically block RNA polymerase (RNAP) to repress gene expression. CRISPRa is achieved by fusing the ω-subunit of the RNAP or the bacterial RNAP activator SoxS to dCas9, and activates transcription by recruitment of the RNAP assembly.