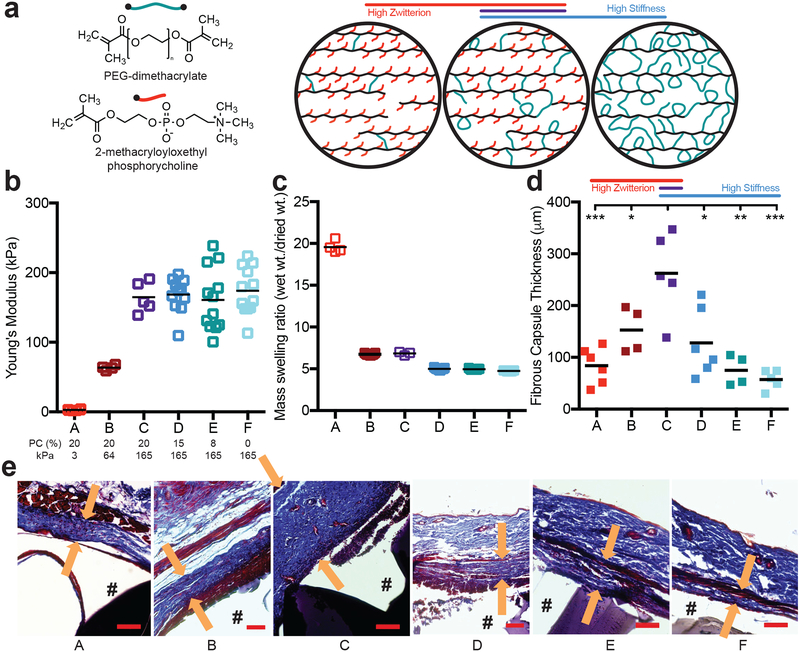
Figure 1. The FBR to PEG hydrogels is highest on stiff, highly zwitterionic implants.
a) A schematic of the hydrogel composed of PEG-dimethacrylate (PEG, green) and 2-methacryloxyloxethyl phosphorycholine (PC, red) to produce a polymer backbone chain (black) with pendant PC groups and PEG crosslinks. b) The Young’s modulus and c) mass swelling ratio of the different hydrogel conditions as both PEG and PC content was modulated (N≥4). The molar percentage of PC and the Young’s modulus for each hydrogel is labeled below b. d) 28 days after hydrogels were subcutaneously implanted into a mouse, the fibrous capsule thickness was measured using a Masson’s Trichrome stain (N≥4). The asterisks indicate significance from hydrogel condition C. e) Representative images for each stain, where “#” denotes the location of the hydrogel, and the arrows represent the thickness measurement taken (scale bar = 100 μm). Significance was determined using an ANOVA with Tukey’s post-test, where p=0.05 was considered significant.