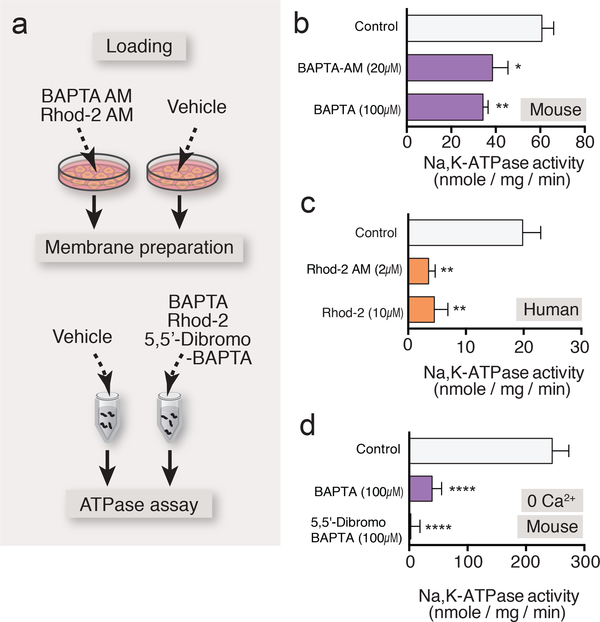
Fig. 3. Ca2+ indicators directly inhibited Na,K-ATPase and diminished the GPCR-mediated enhancement of K+ uptake.
(a) Schematic diagram outlining the ATPase assay with AM and salt form of BAPTA or Rhod-2 in membrane preparation. (b) Addition of BAPTA tetrapotassium salt (100 μM) to membrane preparation induced significant inhibition of Na,K-ATPase activity, which was comparable to that induced by preincubation of BAPTA AM (20 μM) in cultured mouse astrocytes (n=8–14 wells). (c) Effect of Rhod-2 tripotassium salt (10 μM) on ouabainsensitive ATP hydrolysis in membrane preparation compared to the preincubation of Rhod-2 AM (2 μM) in cultured human astrocyte (n=8 wells). (d) Na,K-ATPase activity measurement in the absence or presence of BAPTA tetrapotassium salt (100 μM) or low Ca2+ affinity 5,5’-dibromo BAPTA tetrapotassium salt (100 μM) in the zero Ca2+ assay buffer in cultured mouse astrocytes (n=8–14 wells). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ****p<0.0001 compared to vehicle control (b and d, 0.1% DMSO; c, 0.04% DMSO). Displayed are means ± S.E.M.