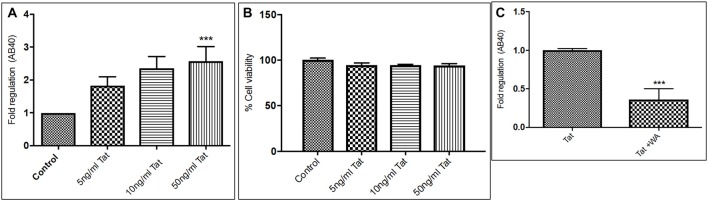
Figure 4.
Tat induce increase in secreted Aβ40 levels (A). Human Amyloid Beta ELISA analysis showing that Tat (5–50 ng/mL) increased the secreted Aβ1–40 significantly in SH-APP cells. (B) Cellular toxicity assay showing viability of the cells in the Tat treated samples. (C) 2μM WA reduced the Tat levels significantly when compared to Tat (50 ng/mL) only treated samples. 1× 106 SH-APP cells were seeded in 6-well plates and were grown for 48 h and then treated with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-1 Tat in different doses and the cells were then incubated for 48 h at 37°C. The supernatant from the culture was collected and treated with protease inhibitor (1μl/ml) and analyzed by Aβ1–40 ELISA (Sigma). The results are from three independent experiments and the statistical significance was calculated by Student’s t-test. Cell viability study was performed by Trypan blue live dead screening, to study the toxicity levels of various Tat dose. Dose selected for Tat treatment for further experiment was elected on the basis of increase in Aβ40 secretion levels and correlated with cell viability (***p ≤ 0.001).