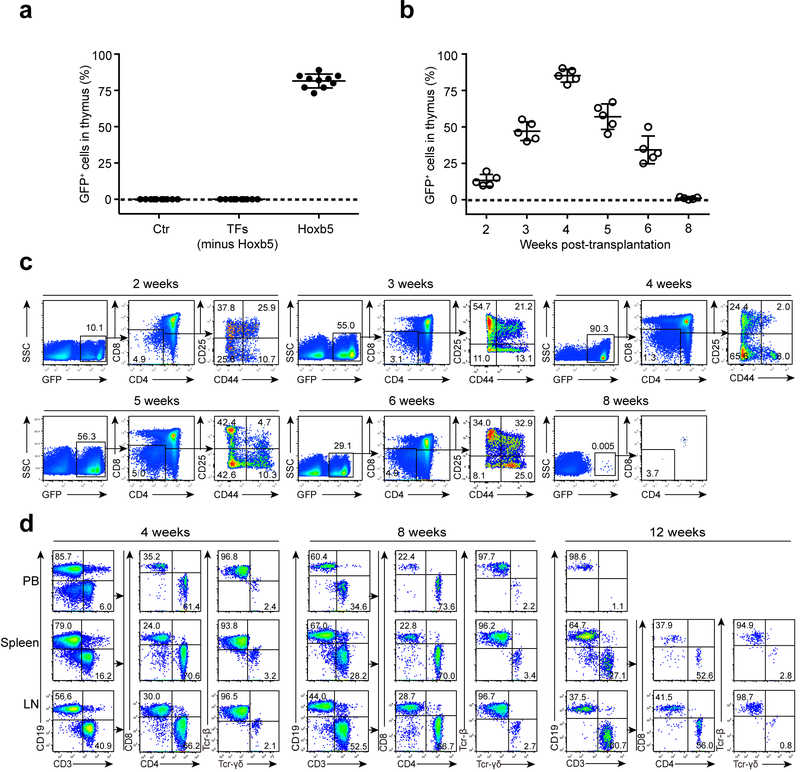
Figure 2. Expression of retro-Hoxb5 in pro-pre-B cells converts B cells to T lymphocytes in vivo.
(a) Detection of Ter119−Mac1−CD19−GFP+ cells in the thymus of recipients transplanted with Hoxb5 virus, GFP-control virus, or 14-factor virus cocktail lacking retro-Hoxb5 transduced pro-pre-B cells. Pro-pre-B cells transduced with the virus mentioned above were transplanted into sublethally irradiated individual congenic mice. Four weeks after transplantation, the Ter119−Mac1−CD19−GFP+ cells in thymus were analysed by flow cytometry (n = 10 mice). Each symbol represents an individual mouse, and small horizontal lines indicate the mean (± s.d.). (b) Kinetics of appearance of GFP+ thymic cells in Hoxb5 recipient mice (n = 5 mice). Each symbol represents an individual mouse, and small horizontal lines indicate the mean (± s.d.). (c) Representative flow cytometry data showing kinetics of appearance of GFP+ cells in the thymus of retro-Hoxb5 mice 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 8 weeks post-transplantation. (d) Dynamics of GFP+ T lymphocytes in PB, Spleen, and LN gated from GFP+Ter119−Mac1− population of retro-Hoxb5 mice. Representative data from 4, 8 and 12 weeks post-transplantation were shown. Data are pooled from three independent experiments (a) or are representative of two independent experiments (c, d).