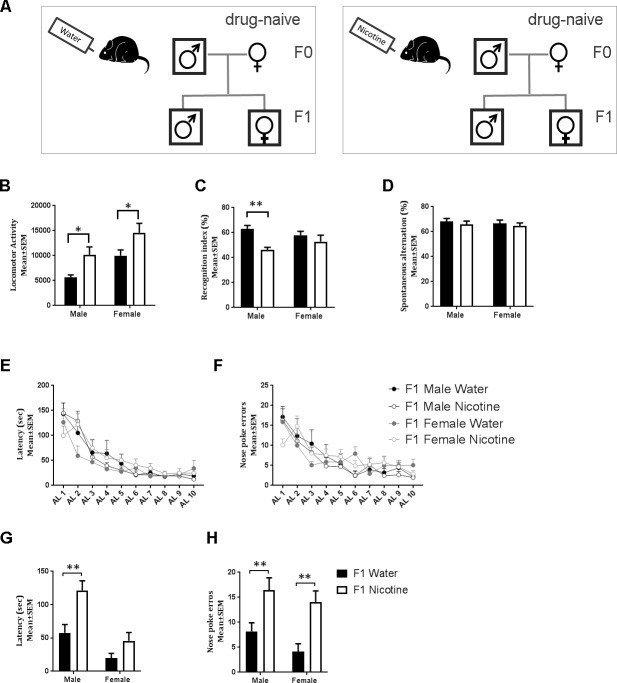
Fig 1. Paternal nicotine exposure paradigm and behavioral phenotypes in F1 male and female mice.
(A) Paternal exposure to nicotine in drinking water and production of F1 mice. (B) Spontaneous locomotor activity was measured in F1 mice over a 12-h period (19:00 to 07:00 h; lights-off period; F1 water male n = 18; F1 nicotine male n = 12; F1 water female n = 13; F1 female nicotine n = 11). (C) Attention was assayed using recognition index in an object-based attention test (F1 water male n = 8; F1 nicotine male n = 7; F1 water female n = 9; F1 female nicotine n = 7), and (D) spatial working memory was assayed using spontaneous alternation index in a Y-maze (F1 water male n = 12; F1 nicotine male n = 13; F1 water female n = 10; F1 female nicotine n = 10). A Barnes Maze was used to measure acquisition learning and reversal learning based on latency to escape (panel E and G) and nose poke errors (panel F and H) (F1 water male n = 8; F1 nicotine male n = 11; F1 water female n = 8; F1 female nicotine n = 11). Data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA. When main effect or interaction was significant, the ANOVA was followed by Bonferroni post hoc test. Asterisks for post hoc comparisons **p < 0.01 and *p < 0.05 (S1 Data).