Figure 3.
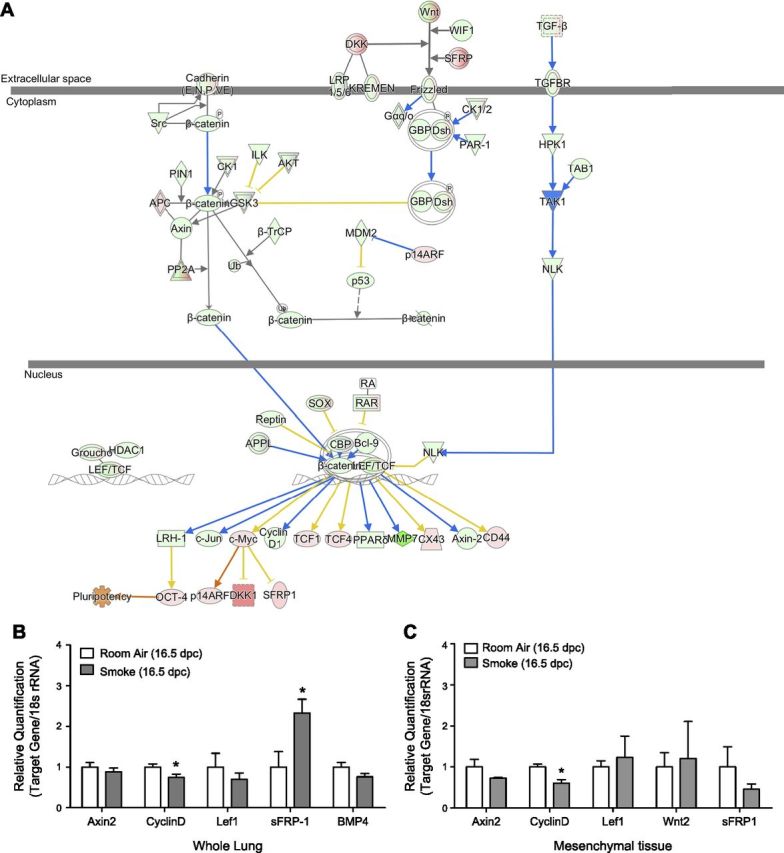
A) Overlay of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway with 16.5 dpc transcriptomic data. Gene expression states of Wnt signaling genes after maternal smoke exposure predict that up-regulation of SFRPs and down-regulation of frizzled receptor will lead to phosphorylation and ubiquitination of cytosolic β-catenin, preventing its translocation to nucleus. At these expression states, LEF/TCF-mediated repression of transcription of Wnt downstream targets CyclinD1, Axin2, and Mmp7 is predicted, as shown, causing decreased cell proliferation phenotypically observed in our studies. B, C) Comparative Wnt signaling in room air– and smoke-exposed fetal mouse lungs. B) qPCR analysis resolves smoke-induced up-regulation of sFRP-1 in 16.5 dpc fetal mouse lungs and down-regulation of Cyclin D1, validating RNA sequencing results presented in A. These expression states account for decreased cell proliferation rates in whole lung homogenates. C) Correlative results obtained from LCM mesenchymal tissue show Cyclin D1 is similarly down-regulated.
