Figure 2.
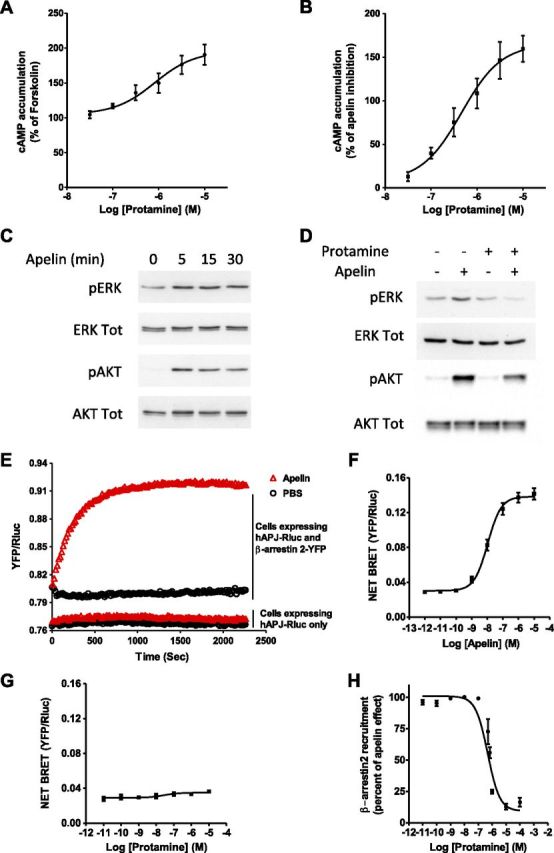
Antagonist activity of protamine on intracellular responses induced by apelin. A) Intrinsic activity of protamine on Gi/o activation via APJ. U2OS cells that stably expressed hAPJ and β-arrestin 2-GFP were stimulated with protamine in the presence of forskolin (20 µM). cAMP production was normalized to the percentage of forskolin-stimulated cAMP accumulation (set at 100%). B) Dose-response curve of protamine for blocking adenylyl cyclase inhibition induced by apelin 13 (10 nM) in the presence of forskolin (20 µM). C) Apelin 13 (100 nM) promotes time-dependent phosphorylation of p42/p44 ERKs and Akt proteins in U2OS cells that stably expressed hAPJ and β-arrestin 2-GFP. D) Protamine pretreatment (1 µM) inhibits ERKs and Akt phosphorylation induced by apelin 13 (100 nM) in the U2OS cells that expressed hAPJ and β-arrestin 2-GFP. E) Real-time measurement of β-arrestin 2 recruitment to APJ measured by BRET in HEK293T cells that expressed hAPJ-Rluc and β-arrestin 2-YFP after addition, at time 0, of 1 µM apelin 13 (▵) or PBS (O). As a negative control, similar experiments were carried out on cells that transiently expressed only Rluc-tagged hAPJ. F, G) Dose-response curve of apelin 13 (F) or protamine (G) for β-arrestin 2 recruitment to APJ measured by BRET in HEK293T cells that transiently coexpressed hAPJ-Rluc and β-arrestin 2-YFP. H) Protamine dose-dependently inhibits β-arrestin 2 recruitment to APJ induced by apelin 13 (100 nM). Data are expressed as the percentage of the maximal BRET signal obtained in HEK293T cells that transiently coexpressed Rluc-tagged hAPJ and YFP-tagged β-arrestin 2 stimulated with apelin 13 at 100 nM (100%). Data represent means ± sem of 5 (A, B), 21 (F), 6 (G), and 4 (H) independent experiments or are representative of 1 experiment performed 3 times independently (C, D, E).
