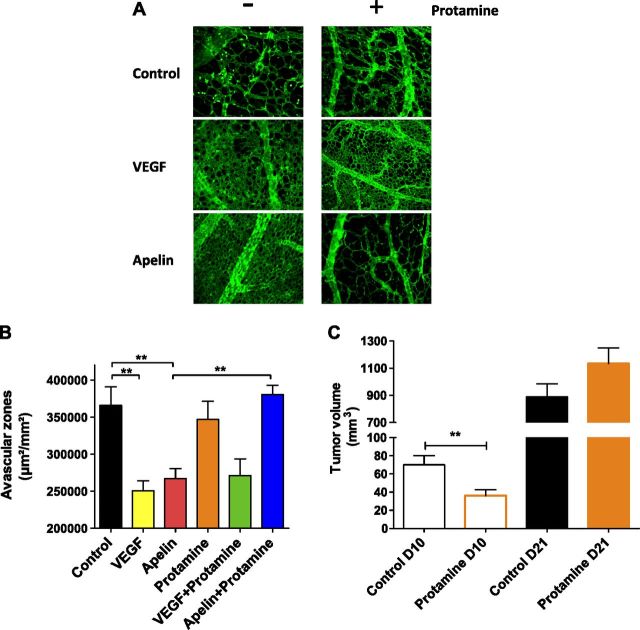
Figure 4.
Antiangiogenic and antitumor activity of protamine is mediated via antagonism of APJ. A) Images of representative CAMs for each condition [PBS, top; VEGF165 (500 ng), middle; apelin 13 (50 ng), bottom] are shown in the absence (left) or presence of protamine (15 µg; right). Blood vessels (green) are visualized by using fluorescein-labeled S. nigra lectin. B) Angiogenic activity of apelin and VEGF and antiangiogenic activity of protamine were quantified by measuring the surface of avascular zones in the CAM assay. Data represent means ± sem of 20 (control, apelin, and VEGF + protamine), 15 (VEGF and protamine alone), and 25 (apelin + protamine) CAMs. Statistical significance was assessed by using 1-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni posttest. **P < 0.01. C) Effect of subcutaneous injection of protamine (5000 U/kg) twice per day on tumor volume (TS/A tumor cell line overexpressing apelin) compared with saline solution–treated mice. Tumor volume on days (D) 10 and 21 are presented. Statistical significance was assessed by using unpaired Student’s t test. **P < 0.01; n = 17 animals per group.