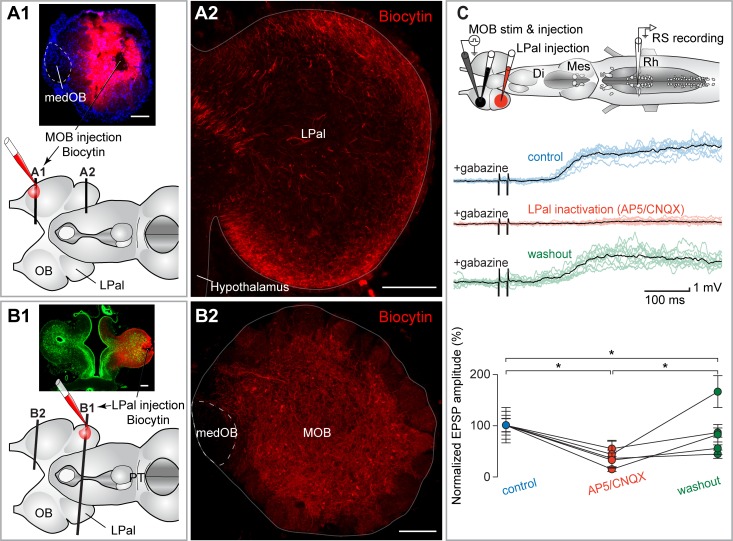
Fig 6. The MOB inputs to RS neurons are relayed in the LPal.
(A1) Schematic representation of the brain illustrating the injection site in the MOB and the level of the cross sections shown in A1 and A2. (A2) Numerous fibers were labeled anterogradely in the LPal after a biocytin injection that included a large portion of the MOB but spared the medOB (see A1). (B1) Schematic illustration of the brain showing the injection site in the LPal and the level of the cross sections shown in B1 and B2. (B2) Projection neurons in the MOB were retrogradely labeled after an injection of biocytin in the LPal. These neurons were mainly located in the external portion of the ICL, close to the glomeruli, as opposed to the GABA-containing neurons that were more internally located in the ICL (Fig 1A and S1 Fig). The level of the injection in the LPal in B1 is similar to the level of the section illustrated in A2. Note that the medOB, which contains neurons that project directly to the PT, does not contain neurons projecting to the LPal. (C) Top: schematic illustration of the brain showing stimulation, injection, and recording sites. Middle: responses of RS neurons to the electrical stimulation (15 μA) of the MOB after injecting gabazine (0.1 mM) in the MOB. A local injection of glutamate receptor antagonists AP5/CNQX (0.5 mM/1 mM) in the LPal abolished the RS neuron responses (red traces). Each black trace is the mean of 10 individual responses (colored traces). Bottom: univariate scatterplot showing the normalized (as a percentage of control) EPSP amplitude in control, AP5/CNQX, and washout conditions for all animals. An asterisk (*) indicates a statistically significant difference at the level p < 0.05, while n.s. indicates the absence of statistically significant difference. The numerical values underlying this figure can be found in S1 Data. Scale bars in A, B = 200 μm. AP5, 2-amino-5-phosphonopentanoic acid; CNQX, 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione; Di, diencephalon; EPSP, excitatory postsynaptic potential; ICL, internal cell layer; LPal, lateral pallium; medOB, medial part of the olfactory bulb; Mes, mesencephalon; MOB, main olfactory bulb; PT, posterior tuberculum; Rh, rhombencephalon; RS, reticulospinal; stim, stimulation.