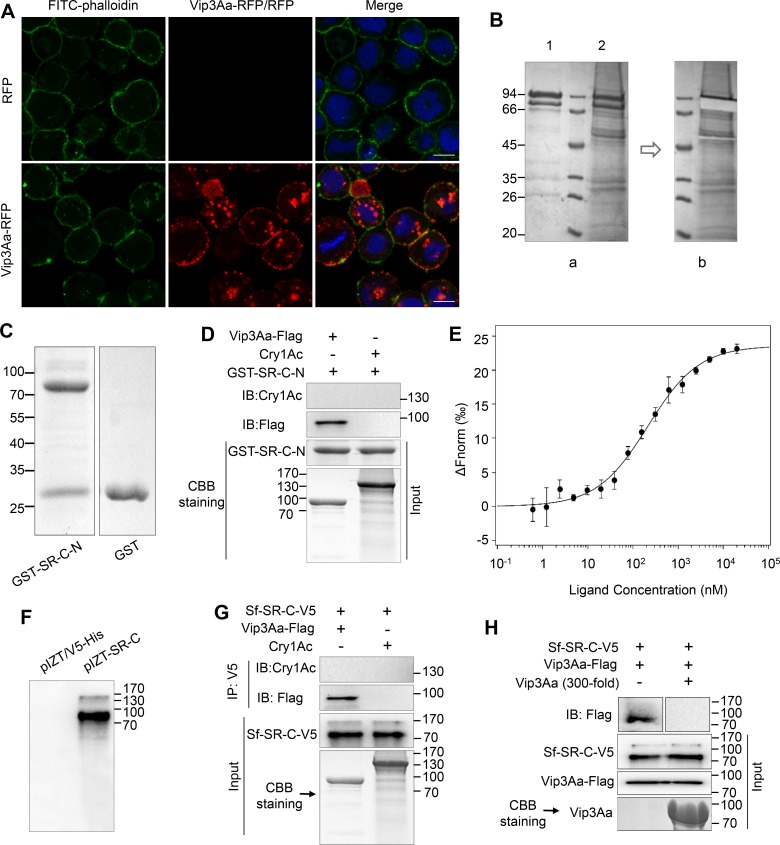
Fig 1. Vip3Aa interacts with Sf-SR-C in vitro.
(A) Confocal microscopy images of Sf9 cells treated with RFP or Vip3Aa-RFP (10 μg/mL) for 3 h. Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue) and cell membrane are stained with FITC-phalloidin (green). Scale bar, 10 μm. (B) Bio-Vip3Aa was incubated with the extracts of Sf9 cell membrane proteins, immunoprecipitated with Streptavidin Mag Sepharose, and detected by Coomassie brilliant blue staining. (a): Lane 1, biotin labeled Vip3Aa; lane 2, the immune complexes. (b): Image of the band of Vip3Aa that was excised from lane 2. (C) The purified GST-Sf-SR-N and GST protein. (D) Vip3Aa-Flag or Cry1Ac were mixed with purified GST-Sf-SR-N, and then the associated complex was pulled down using GST-Sepharose affinity beads followed by immunoblotting (IB) with an anti-Flag antibody or anti-Cry1Ac antibody. (E) MST assay to measure the binding between Vip3Aa and GST-SR-C-N. The labelled Vip3Aa was kept constant at 10 nM, and the GST-SR-C-N is titrated from 0.3 nM to 10 μM. Fitted binding curves and Kd values (mean ± SD) were derived from three independent experiments. (F) Sf9 cells were transiently transfected with the plasmid pIZT-SR-C and the empty vector pIZT/V5-His respectively. 48 h after transfection, cells were collected for immunoblotting with anti-V5 antibody. (G) Sf9-pIZT-SR-C cells lysate was incubated with Vip3Aa-Flag or Cry1Ac, Sf-SR-C in the cells lysate was immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-V5 antibody, Vip3Aa-Flag and Cry1Ac in the elution was detected by immunoblotting with anti-Flag antibody and anti-Cry1Ac antibody respectively. (H) The lysate of Sf9-pIZT-SR-C cells were subjected to SDS-PAGE, and then transferred to PVDF membranes. The PVDF membranes were probed with Vip3Aa-flag or with Vip3Aa-flag plus unlabeled Vip3Aa without Flag-tag (200-fold), followed by immunoblotting with an anti-Flag antibody.