Figure 5. Scale free network and power law distribution.
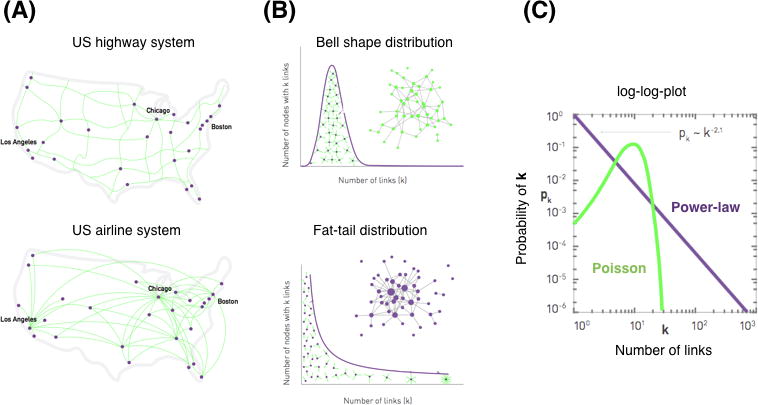
(A) and (B) The US highway system has a bell shape distribution of the number of links (highway connections among cities). By contrast, The US airline system has a fat tail distribution (air routes among airports). (B) For the bell shape distribution (Poisson), most nodes have comparable degrees and nodes with a large number of links absent. The average value of distribution represents the “scale” of the system. The fat tail distribution (Power law) consists of numerous low degree nodes that coexist with a few highly connected hubs. The size of each node is proportional to its degree. The system does not have a mean value and the variance becomes infinite as the system size grows, which is referred to as a “scale free” property. In the log-log plot, the slope of power law distribution categorizes the systems and determines the behavior of scale-free networks.
