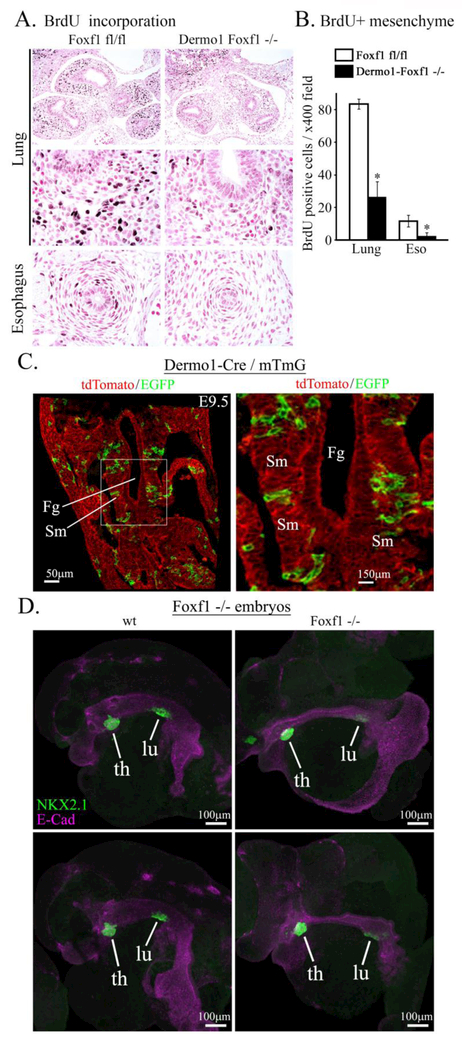
Figure 5. Foxf1 deletion decreases mesenchyme proliferation.
A, Immunostaining of paraffin sections from E11.5 embryos show decreased incorporation of BrdU into mesenchyme of Dermo1-Foxf1−/− lungs and esophagus (dark brown). Slides were counterstained with nuclear fast red (red). B, The number of BrdU-positive cells was decreased in Dermo1-Foxf1−/− lung and esophagus. Ten random x400 microscope fields were counted (n = 5 embryos in each group; * indicates p < 0.05). Magnification: top panels, x100; remaining panels, x400. C, mT/mG transgene was used to show a mosaic pattern of Dermo1-Cre-mediated recombination in mesenchyme surrounding foregut of E9.5 embryos. Images show GFP and tdTomato fluorescence in Dermo1-Cre mTmG embryos. Scale bars are 50μm (left panel) and 150 μm (right panel). D, Global deletion of Foxf1 inhibits lung budding ex vivo. Foreguts with surrounding mesenchyme were micro-dissected from E8.5 Foxf1−/− and control WT embryos and cultured ex vivo for two days. Lung and thyroid buds were visualized by immunostaining for NKX2.1 (TTF1, green) and E-Cadherin (purple). Scale bars are 100 μm. Abbreviations: Fg, foregut; Sm, splanchnic mesenchyme; th, thyroid; lu, lung.