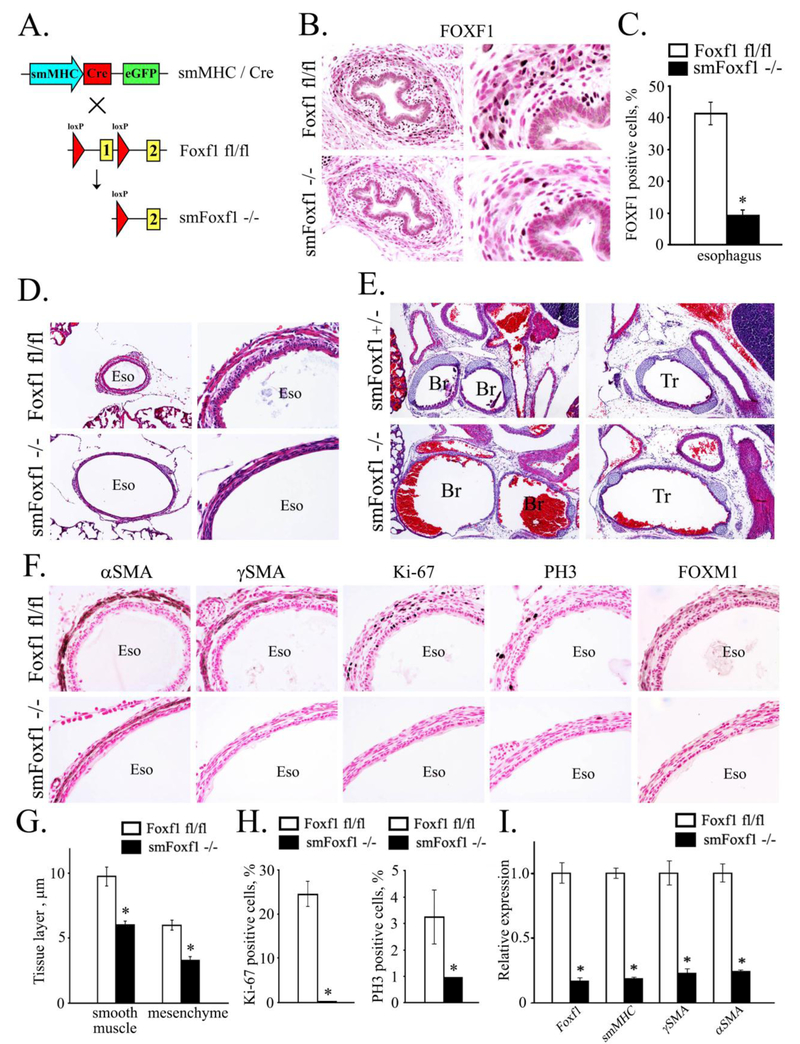
Figure 7. Deletion of Foxf1 from smooth muscle cells causes tracheal and esophageal abnormalities.
A, Schematic drawing shows deletion of Foxf1-floxed allele from smooth muscle cells. Foxf1fl/fl mice were bred with smMHC-Cretg/- mice to generate smMHC-Cretg/- Foxf1fl/fl double transgenic mice (smMHC-Foxf1−/−; abbreviated as smFoxf1−/−). B, Immunostaining for FOXF1 was performed using paraffin sections from E17.5 smMHC-Foxf1−/− and control Foxf1fl/fl embryos. FOXF1 staining (dark brown) was decreased in esophageal smooth muscle of smMHC-Foxf1−/− embryos. Slides were counterstained with nuclear fast red (red). C, The number of FOXF1 -positive cells was decreased in esophageal smooth muscle of smMHC-Foxf1−/− embryos. Ten random x400 microscope fields were used for quantification (n = 3 mice per group; * indicates p < 0.05). D-E, H&E staining shows thinning and hyper-extension of esophagus and trachea in newborn smMHC-Foxf1−/− mice. F, Immunostaining shows reduced smooth muscle cell proliferation in smMHC-Foxf1−/− newborn mice. Immunostaining was performed using antibodies against αSMA, γSMA, Ki-67, PH3 and FOXM1. G, Thickness of esophageal smooth muscle and mesenchymal layers was decreased smMHC-Foxf1−/− newborn mice compared to control Foxf1fl/fl mice (n=3 mice per group). H, Percentage of proliferating cells was reduced in esophageal smooth muscle of smMHC-Foxf1−/− newborn mice. Cells were counted using 10 random x400 microscope fields (n = 3 mice per group). I, qRT-PCR of RNA isolated from esophagus of smMHC-Foxf1−/− newborn mice shows decreased expression of Foxf1, αSMA, γSMA and smMHC. Abbreviations: Eso, esophagus; Br, bronchus; Tr, trachea. Magnification: B (left panels), D (right panels) and F, x400; E and D (left panels), x100; B (right panels), x800.