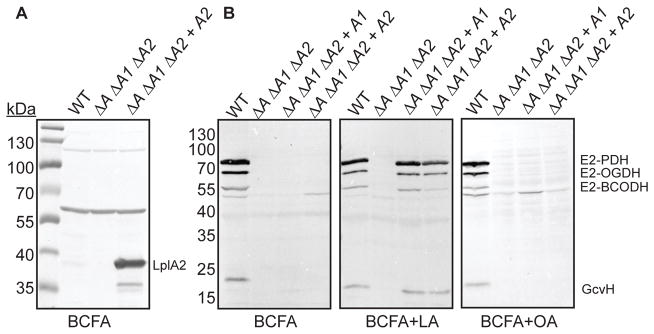
Figure 2. Constitutively expressed LplA1 and LplA2 promote lipoylation in medium containing free lipoic acid.
(A) Immunoblot with α-LplA2 antibody of whole cell lysates derived from the indicated strains grown in RPMI supplemented with branched chain carboxylic acids (10 mM isobutyric acid, 9 mM 2-methylbutyric acid, 9 mM isovaleric acid, and 10 mM sodium acetate - BCFA) in order to bypass the requirement of lipoic acid for replication. (B) Immunoblot with α-lipoic acid antibody of whole cell lysates derived from the indicated strains grown in the same medium as (A) and supplemented with 5 μM lipoic acid (LA) or 150 μM octanoic acid (OA). The positions of the four lipoyl proteins in S. aureus (E2-PDH, E2-OGDH, E2-BCODH, and GcvH) are indicated. Strain designations are as follows: wildtype (WT), ΔlipA ΔlplA1 ΔlplA2 (ΔA ΔA1 ΔA2), ΔlipA ΔlplA1 ΔlplA2 + lplA1 (ΔA ΔA1 ΔA2 + A1), and ΔlipA ΔlplA1 ΔlplA2 + lplA2 (ΔA ΔA1 ΔA2 + A2).