FIG. 5. Effect of alcohol and sepsis on CD4+ T cells.
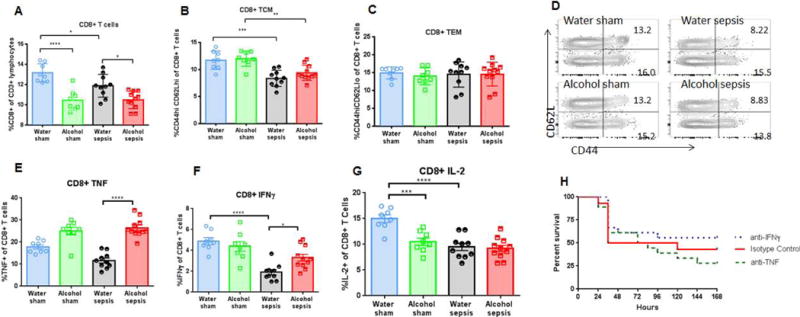
While sepsis in isolation decreased frequency of CD4+ T cells (p=0.03), there was no difference in CD4+ T cell frequency between alcohol-fed septic mice and water-fed septic mice (A, p=0.89). Representative flow cytometry plot for CD4+ T cells is shown (D). Sepsis, in isolation also decreased frequency of central memory CD4+ T cells in both water-fed (p=0.008) and alcohol-fed mice (p=0.005), but there was no difference in central memory CD4+ T cell frequency between alcohol-fed septic mice and water-fed septic mice (B, p=0.39). Effector memory CD4+ T cell frequency was similar in all groups (C, p=0.33 comparing alcohol-septic to water-septic). Representative flow cytometry plot for both central memory and effector memory CD4+ T cells is shown (E). Stimulated cytokine production from CD4+ T cells was similar between alcohol-fed septic mice and water-fed septic mice for TNF (F, p>0.99), IFNγ (G, p=0.052), and IL-2 (H, p=0.84), n=8-11/group for all panels.
