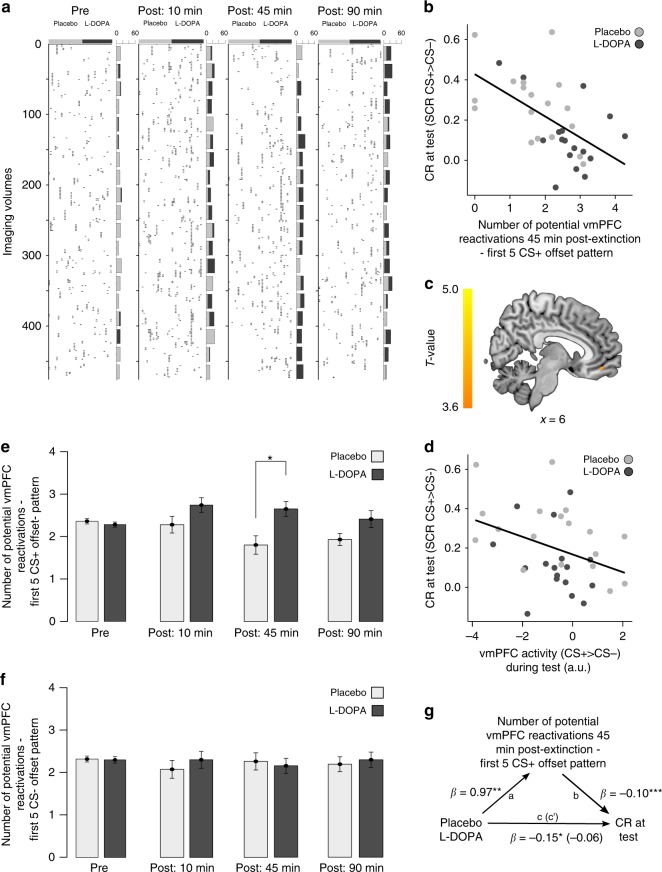
Fig. 2.
Spontaneous postextinction reactivations support extinction memory consolidation. a Temporal distribution of suprathreshold correlations between the spatial fMRI activity pattern in vmPFC evoked on day 2 during extinction by the unexpected US omission (CS+ offsets in early extinction, i.e., first five trials) and the vmPFC pattern occurring at each resting-state volume after extinction on the same day. Each column represents one participant. The bars to the right of each panel represent sum scores per 25 imaging volumes, for both the placebo (light gray) and the l-DOPA group (dark gray). b Relation between the number of potential spontaneous CS+ offset-related vmPFC pattern reactivations 45 min after extinction on day 2 (here and in further graphs expressed as log + 1; for control analyses on nonlog-transformed data, see Supplementary Figs. 2, 3) and CRs at test on day 3 in the whole sample. c The number of potential vmPFC pattern reactivations 45 min after extinction on day 2 predicts CS+ > CS− evoked activity in vmPFC during test on day 3 (SPM multiple regression: MNI x,y,z = 6,46,−14; Z = 3.86, P = 0.01; small-volume (SVC) and family-wise error (FWE) corrected; n = 40). Display threshold P < 0.05, SVC, FWE, no masking applied. d Relation between vmPFC activity and CRs at test on day 3 (Pearson correlation: r35 = −0.37, P = 0.03; n = 35). e Effect of l-DOPA administration after extinction on day 2 on the number of spontaneous reactivations of CS+ offset-related vmPFC patterns during subsequent resting-state scans. f There was no effect of l-DOPA on number of spontaneous reactivations of CS− offset-related vmPFC patterns during resting-state scans on day 2 (repeated-measures ANOVA: time × group: P = 0.63, group: P = 0.77; n = 40). g The postextinction administration of l-DOPA had a significant positive effect on number of potential CS+ offset-related vmPFC reactivations (path a: ß = 0.97, SE = 0.30, T33 = 3.23, P = 0.003; n = 35). The number of potential CS+ offset-related vmPFC reactivations 45 min after extinction was significantly negatively related to smaller differential CRs at test on day 3 (path b: β = −0.10, SE = 0.03, T33 = −4.26, P = 0.0002; n = 35). After inclusion of number of potential CS+ offset-related vmPFC reactivations into the latter model, the significant effect of drug on CRs at test (path c: ß = −0.15, SE = 0.06, T33 = −2.57, P = 0.02; n = 35) decreased (path c’: β = −0.06, SE = 0.06, T32 = −0.98, P = 0.33; n = 35), indicating that the effect of l-DOPA on CRs at test on day 3 was significantly mediated (c–c’ = −0.09, 95% CI: −0.13 to −0.02, P = 0.007; bootstrapping procedure with 10,000 simulations; n = 35) by number of potential CS+ offset-related vmPFC reactivations 45 min after extinction