Fig. 5.
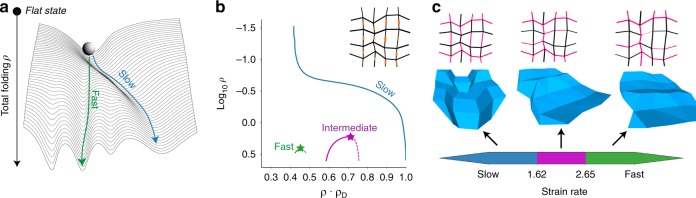
Folding speed can controllably select between different folding pathways. a While slow folding follows the continuous deformation of the unique mode at low strain ρ (blue), fast folding results in a state that most “resembles” that low-ρ mode (green). If the unique low-ρ mode is significantly distorted in geometry relative to the slow folding target, slow and fast folding can result in very different outcomes. b, c We systematically attempted folding at different strain rates (relative to a fixed hinge relaxation timescale) for the 16-vertex pattern with stiff creases shown. We find three distinct outcomes at slow, intermediate, fast rates that completely differ in their Mountain-valley states, geometry and energy. The slow folding outcome corresponds to following the blue path in (b) while the intermediate and fast pathways cross over from blue to the magenta and green modes, respectively, at some intermediate folding angles