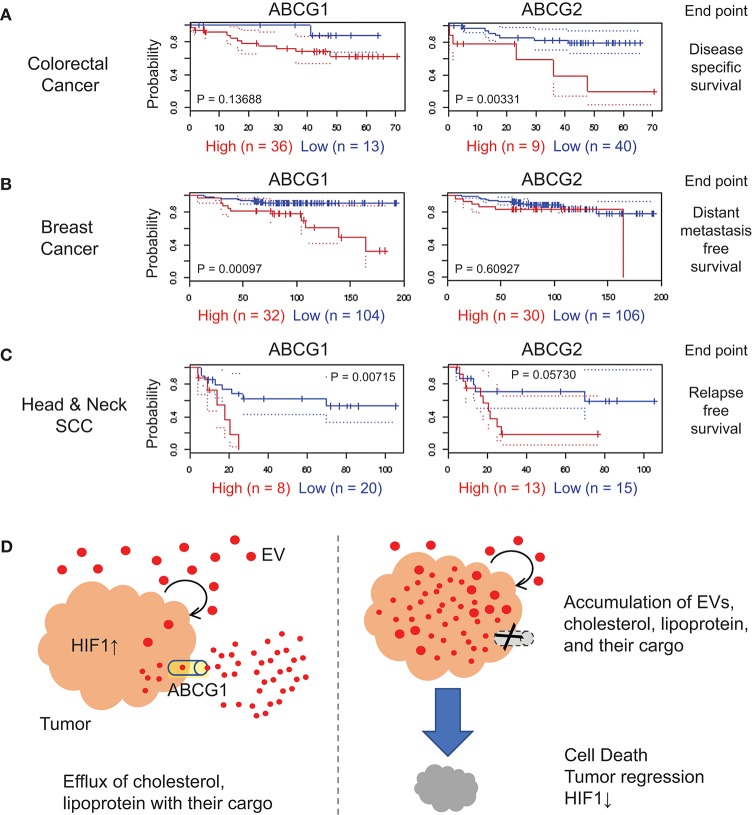
Figure 6.
Correlation of ABCG1/G2 expression levels with cancer prognosis. ABCG1/G2 were analyzed by using PrognoScan and the Kaplan-Meier estimates of the indicated cohort studies were shown with minimum P values. The detailed data were shown in Table S1. Red, the high-level expression group. Blue, the low-level expression group. (A) colorectal cancer with an endpoint of disease-specific survival, (B) breast cancer with an endpoint of distant metastasis-free survival, and (C) head and neck squamous cells carcinoma with an endpoint of relapse-free survival. (D) Roles of ABCG1 in tumor progression and its targeting. Tumor cells secrete redundant metabolites with their EVs and lipoproteins, some of which may be toxic to themselves when accumulated in the tumor cells. ABCG1 plays an efflux role for lipoproteins, cholesterol, and their cargos that may include redundant and cytotoxic substances. The efflux and detoxification role of ABCG1 can promote cancer cell survival and tumor growth with elevated HIF1-α level. In our study, depletion of ABCG1 triggered the accumulation of EVs and death in tumor cells.