Figure 2.
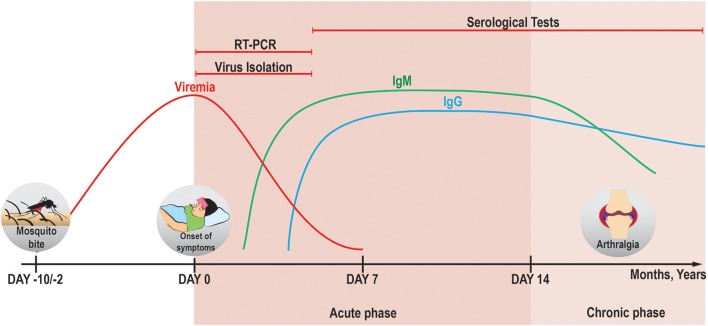
Applicability of different diagnostic methods in the course of CHIKV infection. In the acute phase, viremia can persist until days 5–7 pio (Silva and Dermody, 2017) and CHIKV genomic RNA can be detected by RT-PCR reliably until day 7 pio (Edwards et al., 2017). It is therefore suggested that the detection of CHIKV RNA and virus isolation from serum samples for diagnostic purposes is done before day 5 pio (Johnson et al., 2016b), because the chance of false-negative results increases with the decrease in viral load. IgM and IgG antibodies against CHIKV begin to be produced at days 2 pio (Jain et al., 2018) and 4 pio (Prince et al., 2015), respectively. Stable titers of IgM can be seen in the serum from day 6 pio till around 4 months pio (Prince et al., 2015) [and can be detected mostly until 6 months pio (Chua et al., 2017)], whereas sustained levels of IgG can be present for more than 1 year (Chua et al., 2017). The antibodies against CHIKV can be detected by immunoassays after the development of humoral immune response (in case of IgG–long into the chronic phase, both–symptomatic or asymptomatic). A more detailed overview of the methods available for diagnostics of CHIKV is given in a review by Sam et al. (2015).