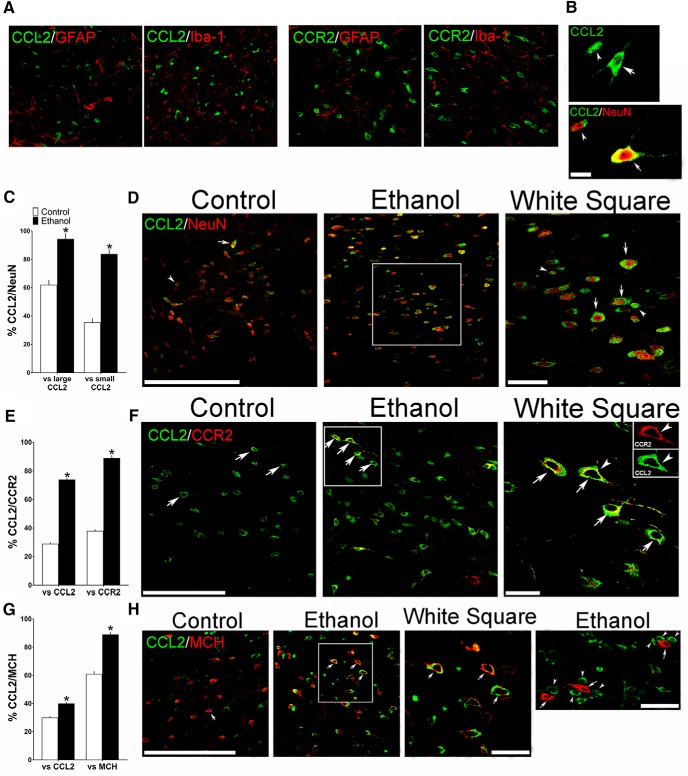
Figure 8.
Maternal ethanol administration (2 g/kg/d, E10–E15) compared with control solution, while having no effect on glia, alters the density of both large and small CCL2+ neurons in the LH, as assessed by IF in female adolescent offspring (n = 7/group). A, Confocal images show in ethanol-treated offspring no colocalization of CCL2 or CCR2 (green) with the markers of astrocytes (GFAP) and microglia (Iba-1) (red). B, Two confocal images provide typical examples of the large (arrow) and small (arrowhead) CCL2+ single-labeled cells (green) in the LH (top) and of large (arrow) and small (arrowhead) CCL2+ neurons that double-labeled the neuronal marker NeuN (bottom), with CCL2 (green) and NeuN (red) revealing CCL2+/NeuN+ double-labeled neurons that are large (yellow/red center) or small (green/red center). C, Maternal ethanol administration increased the density of both large and small CCL2+ neurons that double-labeled NeuN, as indicated by the increased percentage of both large and small CCL2+/NeuN+ double-labeled neurons relative to total large or total small CCL2+ single-labeled cells, respectively. D, Representative confocal images show few large (arrow) and few small (arrowhead) CCL2+ (green) neurons that colabeled NeuN (red) in control offspring (left) but many CCL2+/NeuN+ neurons (green/red center) in ethanol-exposed offspring (middle), with those in the white square illustrated at higher magnification (right). E, Maternal ethanol administration increased the density of CCL2+ neurons, mostly large, that colabeled CCR2, as indicated by the increased percentage of large CCL2+/CCR2+ double-labeled neurons relative to total large CCL2+ or CCR2+ single-labeled neurons. F, Representative confocal images, illustrating mostly large CCL2+ (green) and CCR2+ (red) neurons that were double-labeled (green/yellow), show some CCL2+/CCR2+ neurons (arrow) in control offspring (left) and many more CCL2+/CCR2+ neurons (arrow) in ethanol-treated offspring (middle), with those in the white square illustrated at higher magnification (right). G, Maternal ethanol administration increased the density of CCL2+ neurons, mostly large, that colabeled MCH, as indicated by the increased percentage of large CCL2+/MCH+ double-labeled neurons relative to total large CCL2+ or MCH+ single-labeled neurons. H, Representative confocal images, illustrating mostly large CCL2+ (green) and MCH+ (red) neurons that become yellow/red or green/red when double-labeled, show few CCL2+/MCH+ neurons (arrow) in control offspring (left) and many CCL2+/MCH+ neurons (arrow) in ethanol-treated offspring (middle), with those in the white square illustrated at higher magnification (right). While few small CCL2+ cells were found to double-label CCR2 or MCH, the small CCL2+ cells (arrowhead, green) were sometimes seen adjacent to or surrounding large MCH+ neurons (arrow, red) as shown in at far right. Scale bars: A, 100 μm; B–H, 200 μm. Data are mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 versus control.