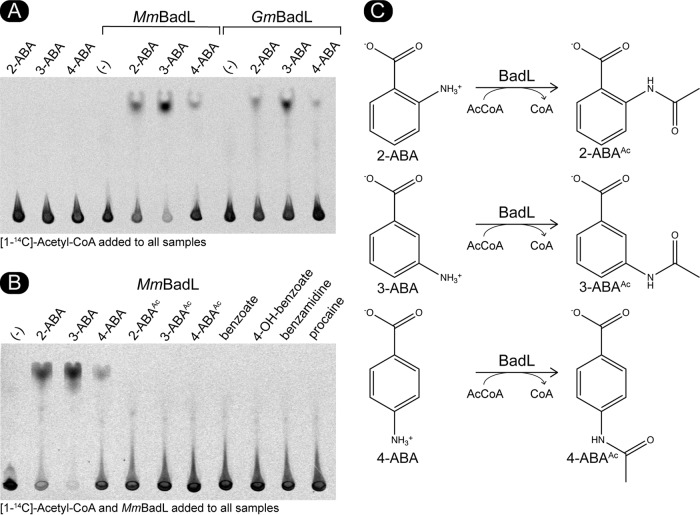
FIG 6.
BadL homologues acetylate aminobenzoates in vitro. (A) MmBadL and GmBadL (3 μg) were incubated with [1-14C]acetyl-CoA and 2-aminobenzoate (2-ABA), 3-aminobenzoate (3-ABA), or 4-aminobenzoate (4-ABA). As a negative control, 2-ABA, 3-ABA, and 4-ABA were incubated with [1-14C]Ac-CoA (three leftmost lanes). The lanes designated by (-) indicate reaction mixtures that contained BadL and [1-14C]Ac-CoA but lacked substrate. The reaction mixtures were spotted onto the gels, and acetylated products migrated away from the origin where [1-14C]-Ac-CoA remained. (B) MmBadL was incubated with various aromatic substrates as listed above each lane. Lanes labeled as 2-ABAAc, 3-ABAAc, and 4-ABAAc indicate reaction mixtures containing authentic acetylated 2-ABA, 3-ABA, and 4-ABA as described in Materials and Methods. Lane designated by (-) identify a reaction mixture where BadL was incubated with [14C-1]Ac-CoA but no substrate. The reaction mixtures were spotted onto gels, and acetylated products migrated away from the origin, where [1-14C]Ac-CoA remained. Images were acquired by exposure to a phosphor screen and subsequent imaging. (C) Proposed reaction schematic of BadL-mediated aminobenzoate acetylation.