FIGURE 1.
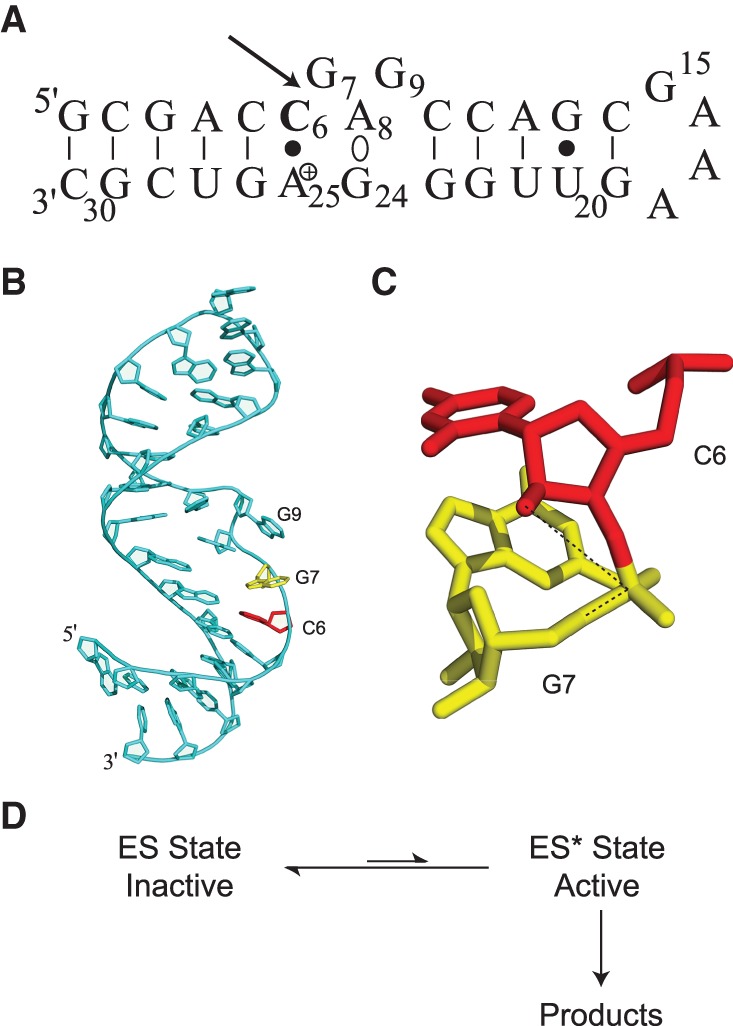
Sequence and three-dimensional structure of the lead-dependent ribozyme. (A) Leadzyme secondary structure, indicating the adenosine residue (Ade-25) with a shifted pKa of 6.5 as positively charged (Legault and Pardi 1997), the noncanonical dynamic A-G base-pairing interaction (Ade-8°Gua-24), and the self-cleavage site (arrow). (B) Overall structure of the leadzyme as observed in solution (Hoogstraten et al. 1998). Residues flanking the cleavage site are colored red (Cyt-6) and yellow (Gua-7). (C) Expanded view of Cyt-6 and Gua-7 (colored as in B), illustrating the lack of in-line alignment for the reactive groups (dotted line connecting nucleophilic O2′, reaction center phosphorus, and leaving group O5′). (D) Schematic reaction scheme for the leadzyme, illustrating the requirement for dynamic sampling of a rare (“invisible”) conformational state ES* for self-cleavage. Structure panels were prepared with PyMol (Delano 2002).
