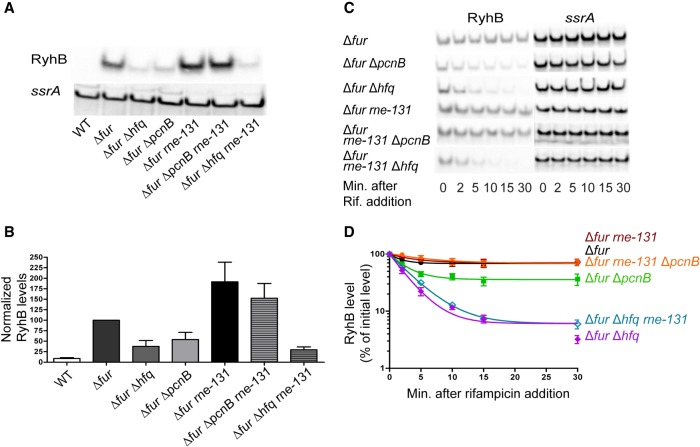
FIGURE 1.
RyhB is rapidly degraded in the absence of poly(A) polymerase in an RNase E-dependent mechanism. (A,B) Northern blot analysis to assess RyhB steady-state levels. Overnight cultures of strain NRD1138 (WT), an isogenic Δfur strain (DS024), or derivatives of this Δfur strain harboring deletions in hfq (DS027), pcnB (DS025), rne (DS069), rne and pcnB (DS082), and rne and hfq (DS153) were diluted 200-fold in fresh MOPS EZ rich defined media supplemented with 0.4% glycerol. All cultures were subsequently grown to late exponential phase (OD600 of 1.0), and samples were collected for RNA extraction. (C,D) RNA stability time course experiment to determine the intrinsic stability of RyhB. Briefly, overnight cultures of the Δfur parent (DS024) and its derived mutant strains (Δfur ΔpcnB, DS025; Δfur Δhfq, DS027; Δfur rne-131, DS069; Δfur rne-131 ΔpcnB, DS082; Δfur rne-131 Δhfq, DS153) were grown to OD600 of 1.0 as described above and a culture sample was taken. Rifampicin was added to each culture to stop total transcription, and additional culture samples were taken 2, 5, 10, 15, and 30 min after rifampicin addition. All samples were subjected to RNA extraction and were prepared for northern blot analysis as described in Materials and Methods. Representative northern blots are shown in A and C. (B,D) RyhB signal intensities in the northern blots were quantified and normalized to their corresponding loading controls (ssrA). sRNA decay curves were generated by fitting the normalized signal intensities for each time point. Points and error bars in the curves represent the means and the standard errors (SEM) of at least three independent experiments. RyhB half-life measurements corresponding to RNA stability curves (D) are listed in Table 1.