FIGURE 4.
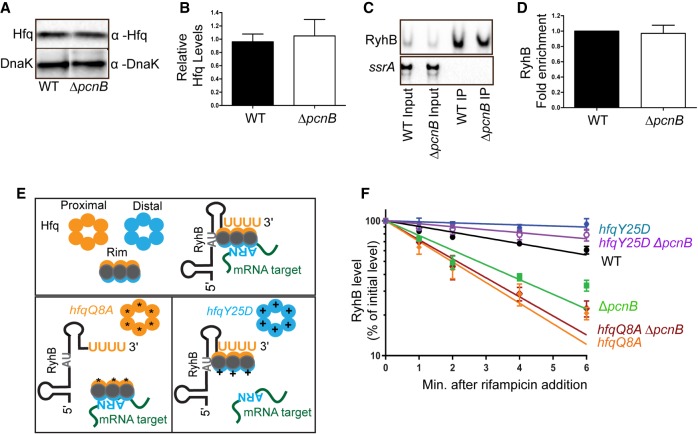
The accelerated decay of RyhB in the absence of poly(A) polymerase is mediated by Hfq. (A,B) Western blot analysis to determine Hfq protein levels. Samples were prepared for western blotting from exponential phase cultures of a fur+ strain (DS090), and its derived strain ΔpcnB (DS092) with anti-Hfq antibody. Protein band intensities were normalized to DnaK detected with an anti-DnaK antibody (Materials and Methods). Representative western blots are shown in A. Quantification of Hfq levels from those western blots normalized to DnaK levels are shown in B. (C,D) Coimmunoprecipitation of RyhB with Hfq. RyhB expression was induced in exponential cultures of a wild-type (NRD1138) and an isogenic ΔpcnB mutant (NRD1198). Hfq was immunoprecipitated with anti-Hfq antibody bound to protein-A-sepharose. RNA extracted from the input and elution fractions were loaded in 1:8 ratio, and RyhB and ssrA levels were determined via northern blot analysis (C). Fold enrichment of RyhB (D) was determined after quantification of the RyhB and ssrA signal intensities in those northern blots as described in Materials and Methods. (E) Schematic showing interactions between RyhB, mRNA targets, and Hfq based on work by Schu and coworkers (Zhang et al. 2013; Schu et al. 2015); a Q8A substitution in the proximal face of Hfq was shown to disrupt RyhB binding, whereas a Y25D substitution in the distal face of Hfq reduced binding of RyhB target mRNAs such as sodB. (F) RNA half-life experiments to determine RyhB stability in the wild-type strain and its derived isogenic hfq and pcnB mutants. Overnight cultures of the wild-type strain (WT [fur+]; NRD1138) and its derived mutants (ΔpcnB, NRD1198; hfqQ8A, DS060; hfqY25D, NRD1410; hfqQ8A ΔpcnB, DS072; hfqY25D ΔpcnB, DS185) were diluted 200-fold in fresh LB media. Cultures were subsequently grown to exponential phase, dipyridyl was added to induce RyhB expression, and a culture sample was taken after 15 min of induction. Rifampicin was added to each culture to stop total transcription, and additional culture samples were taken 1, 2, 4, and 6 min after rifampicin addition. RNA extraction and northern blot analysis were performed as described above. Representative northern blots are shown in Supplemental Figure S5 of Supplemental Information. For decay curves, RyhB signal intensities from the northern blots were quantified and normalized to their corresponding loading controls (SsrA). Data shown in B, D, and F represent the means and the standard errors (SEM) of at least three independent experiments. RyhB half-life measurements corresponding to RNA stability curves are listed in Table 1.