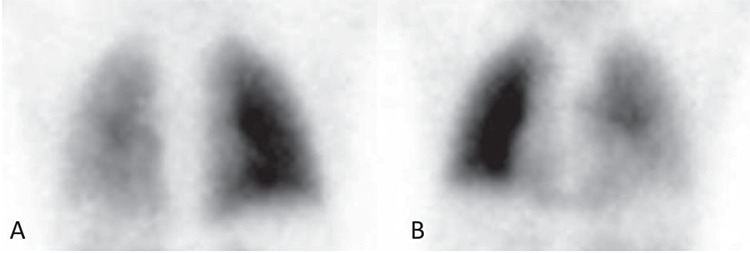
Figure 2. LPS is a functional diagnostic tool that records the distribution of pulmonary arterial blood flow. The most common clinical indications for LPS are to detect pulmonary embolism, to quantify differential pulmonary perfusion before surgery or in chronic disorders, to evaluate the cause of pulmonary hypertension and assessment for lung transplantation. In patients with CHD, LPS evaluates the co-existence of congenital heart and lung hemodynamic defects such as cardiac shunt, pulmonary arterial stenosis, arteriovenous fistula and their treatment (4). LPS can depict normal symmetrical perfusion, unilateral absent or decreased perfusion, or multiple segmental abnormalities in patients with CHD. It allows to define the presence of a right to left shunt due to the presence of aortic-pulmonary collaterals vessels, associated with cyanogenic CHDs such as TOF (5). This LPS figure shows the thorax in detail, in the posterior (A) and anterior (B) projections, which clearly depicts hypo-perfusion of the left lung as compared to the right.