FIGURE 4.
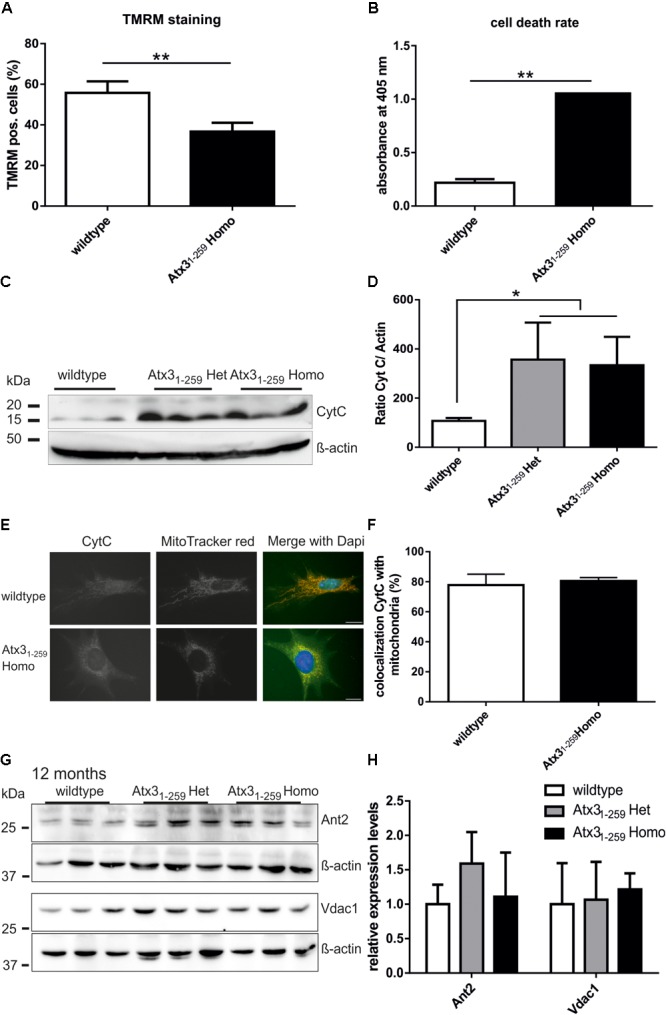
Reduced mitochondrial membrane integrity and higher rate of apoptosis were found in homozygous Atx31-259 MEF. (A) Mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), a marker for mitochondrial membrane integrity, was determined in MEF by TMRM treatment for 30 min at 37°C and subsequent FACS analyses. In five independent experiments a significant reduction of MMP was found in homozygous Atx31-259 MEF compared to wildtype cells (∗∗p < 0.01). (B) Measuring the cell death rate using a cell death-detection kit revealed significantly more apoptosis in homozygous Atx31-259 MEF compared to wildtype MEF (∗∗p < 0.01, n = 3). (C,D) As indicator for mitochondrial-associated apoptosis in whole brain lysates of heterozygous and homozygous Atx31-259 mice, the protein level of free cytochrome C was measured in three mice per genotype at the age of 12 months. Densitometric quantification revealed significantly more free cytochrome C in heterozygous and homozygous Atx31-259 mice compared to wildtype controls (∗p < 0.05). (E,F) Immunofluorescence staining of cytochrome C in MEF cells revealed a disrupted mitochondrial network in Atx31-259 homozygous MEF and a good overlap of cytochrome C with mitochondria in both genotypes. (G,H) Analyzing protein levels of members of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (Ant2, Vdac1) in whole brain lysates of 3 mice per genotype also did not identify differences in protein expression at the age of 12 months, which was confirmed by densitometry quantification (G). β-actin is shown as loading control.
