Figure 4.
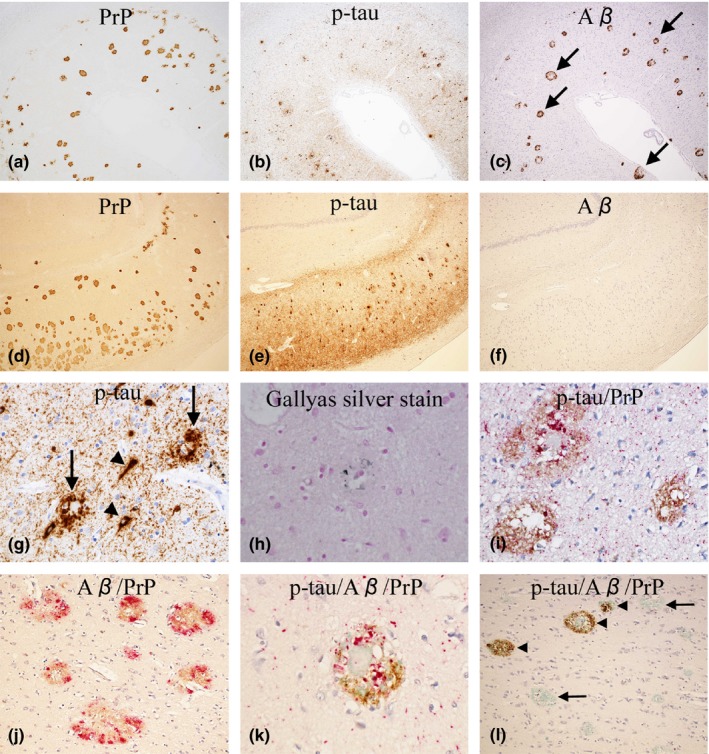
Case 2: (a–c, d–f) The distribution of PrP (a, d), p‐tau (b, e), and Aβ (c, f) in the temporal cortex (a–c) and hippocampus (CA1 to subiculum, d–f) is shown. The photos are taken from an identical area for a–c and d–f. In the temporal cortex (a–c), p‐tau (b, AT8‐immunostain) and Aβ (c, 4G8‐immunostain) seem considerably overlapped with PrP (a, 3F4‐immunostain). Notably, most deposits of Aβ have an immuno‐negative central core (arrows, c). In the hippocampus (d–f), p‐tau (e, AT8‐immunostain) seems considerably overlapped with PrP (d, 3F4‐immunostai), whereas Aβ (f, 4G8‐immunostain) is totally absent. (Original magnification: a–c, ×40; d–f, ×40). (g) P‐tau‐positive dystrophic neurites (DNs) around PrP‐plaques (arrows), neurofibrillary tangles (arrowheads), and neuropil threads are commonly seen (AT8‐immunostain, temporal cortex, ×400). (h) A small fraction of DNs around PrP‐plaques are argyrophilic (Gallyas silver stain, frontal cortex, x600). (i) By double‐immunostaining with AT8 and PrP‐N, the colocalization of p‐tau with PrP‐plaques is confirmed. (p‐tau, red; PrP, brown. Temporal cortex, x400). (j) By double‐immunostaining with 4G8 and PrP‐N, the deposition of Aβ around PrP‐plaques is confirmed. Note that most Aβ is colocalized with PrP. (Aβ, red; PrP, brown. Temporal cortex, ×200). (k) By triple‐immunostaining with AT8, 4G8, and PrP‐N, the colocalization of p‐tau, Aβ, and PrP is confirmed (p‐tau, red; Aβ, brown; PrP, green. Temporal cortex, ×600). (l) By triple‐immunostaining with AT8, 4G8 and PrP‐N, it is also shown that PrP, with or without p‐tau, can be present without Aβ (arrows); on the other hand, Aβ, with or without p‐tau, cannot be present without PrP (arrowheads), suggesting that PrP deposition is likely a precursor event to Aβ deposition. (p‐tau, red; Aβ, brown; PrP, green. Temporal cortex, ×600)
