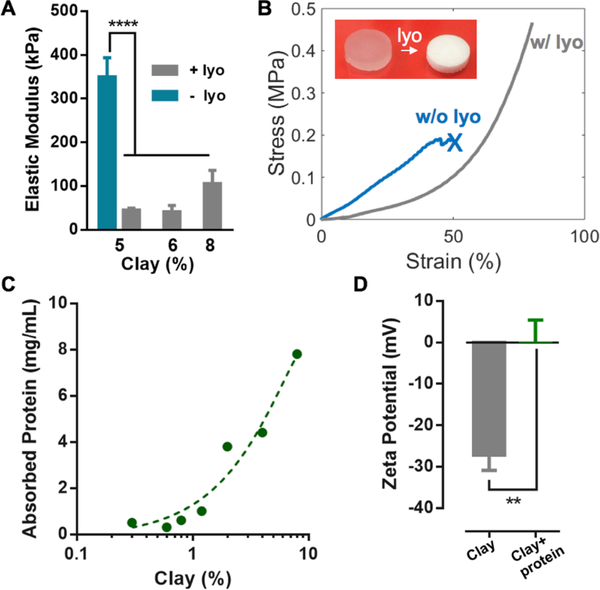
Figure 2.
Drug-loading and mechanical properties of the composite hydrogels. A) Elastic moduli of the composite hydrogels with different clay contents; the as-prepared hydrogels of 5% clay before lyophilization (blue bar) is included for comparison. Data represents the mean ±SD; N=3 per group. P values were determined by an ANOVA test; ****P≤0.0001. B) Compression stress-strain curves of the composite hydrogels (6% clay) before (w/o lyo) and after lyophilization (w/ lyo); the cross indicates gel rupture. The inset shows the composite hydrogels before and after lyophilization. C) Dependence of the IGF1 mimetic protein loading capacity on the clay content. The initial concentration of the protein was fixed at 8 mg/mL. D) Zeta potentials of the clay nanoparticles with and without adsorbed IGF1 mimetic protein. Data represents the mean ±SD; N=3 per group. P values were determined by a student t test; **P≤0.01.