Fig. 7.
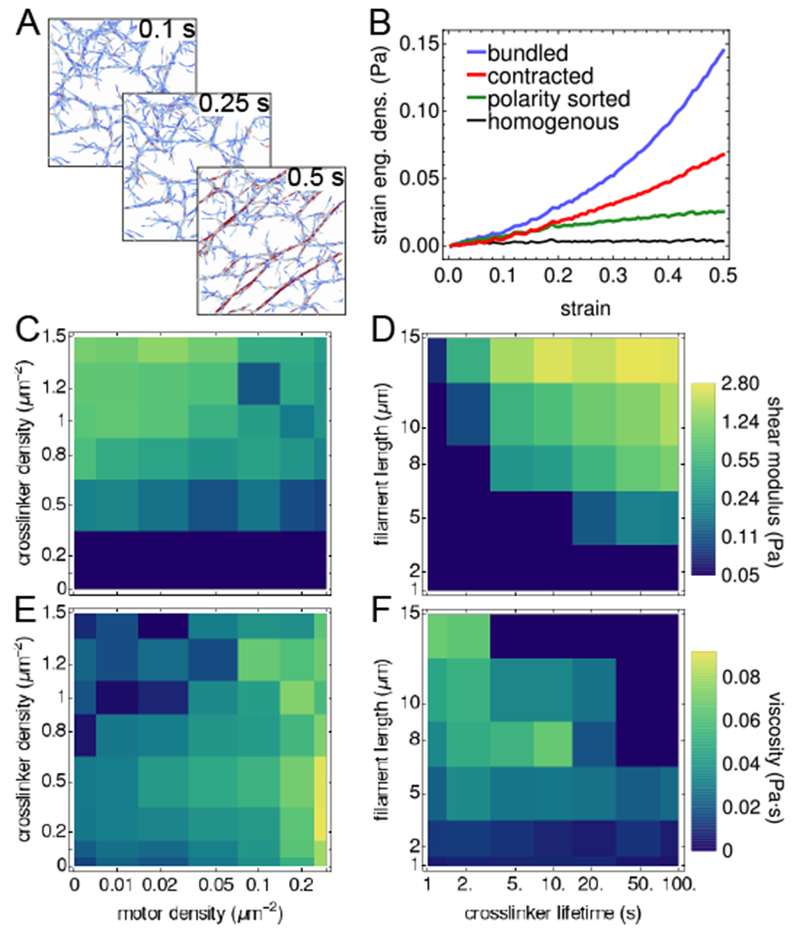
Elasticity of network structures. (A) Shearing a bundled network for 0.5 s at a strain rate of . Depth of color indicates stretch of filament. (B) Viscoelastic response of the network to a simple shear, as measured by the dependence of the strain energy density on the strain. (C-D) Shear modulus of structures (shown in Fig. 1) formed with constant filament length (L = 10 μm) and lifetimes (), but different motor and crosslinker densities (C), and for structures (shown in Fig. S7) formed without motors and constant crosslinker density (ρxl = 1.2 μm−2), with different filament lengths and crosslinker lifetimes (D). (E-F) Viscosity of these networks. Strain calculations in (B-F) are averaged over 5 independent trajectories.
