Figure 4. Perforin-Deficient Animals Have Enhanced GC Expansion and Somatic Mutation Rates Comparable to NK-Cell-Depleted Animals.
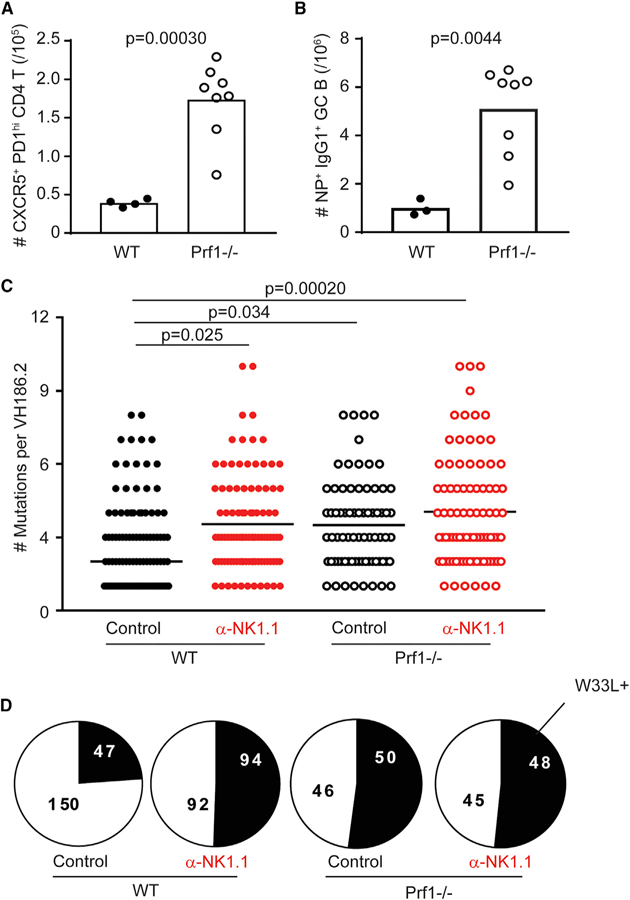
(A) Total number of GC TFH (CD4+CD44hiCXCR5+ PD-1hi) cells in the spleen of C57BL/6 (WT) or perforin-deficient (Prf1−/−) control-treated (mIgG2a) animals day 12 post-NP-KLH immunization.
(B) Total number of NP+IgG1+ GC B (CD19+B220+ Fas+GL-7+) cells. Data were analyzed via Stu-dent’s t test; n = 3–8 mice/group.
(C) Total number of mutations in control or α-NK1.1-treated WT or Prf1−/−animals day 12 post-immunization. Data were analyzed via Kruskal-Wallis with multiple testing correction; n = 5–6 mice/group.
(D) Proportion of unique VH186.2 sequences from (C) bearing W33L mutation. Experiments were repeated 2 or 3 times.
