Fig. 1. Structures of LARKS (B-F) compared to a steric zipper (A).
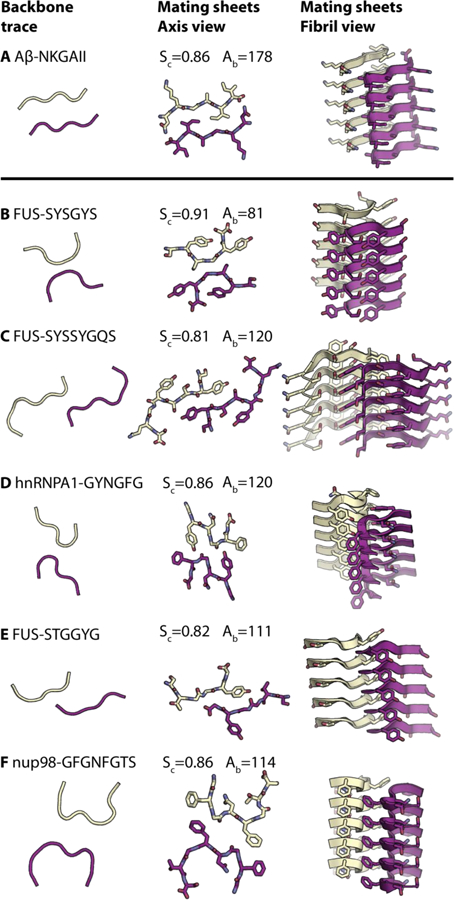
All structures composed of two mating β-sheets, one purple and the other yellow. The left-hand column shows the trace of the backbones of mating sheets to highlight kinks in the backbones of LARKS and the pleating of the classical β-sheets in steric zippers. The second column shows the atomic structures of mating sheets viewed down the fibril axes. The third column shows cartoons of the mating β-sheets viewed nearly perpendicular to the fibril axes. Each interface is characterized by the shape complementarity score (Sc=1.0 for perfect complementarity) and buried solvent-accessible surface area (Ab) in Ų between the mated sheets. Carbon atoms are colored purple or yellow, Nitrogen is blue, and Oxygen is red. Five layers of β-sheets are shown of the hundreds of thousands in the crystals. The kinked structures of LARKS are rare among mating β-sheets; dozens of other paired β-sheets form steric zippers (35).
