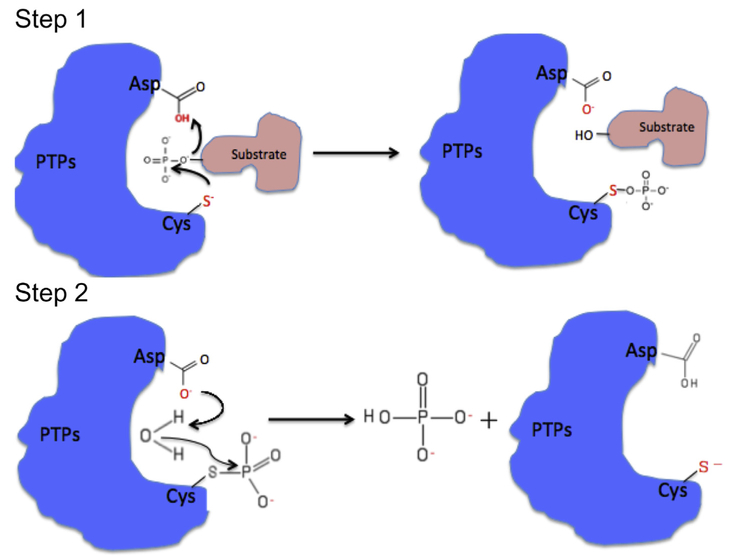
Fig. 2.
Two-step catalytic mechanism of PTPs. PRLs share a canonical two-step catalytic mechanism with other PTPs. In step one, the thiolate anion of the Cysteine residue in the P-loop acts as a nucleophile, attacking the phosphate group on the substrate then forming a thiophosphoryl enzyme intermediate, and the second aspartate reside in the WPFDD loop acts as a general acid by donating a proton to the leaving group in the substrate. In step two, the same aspartate residue acts as a general base by activating a water molecule that can hydrolyze the enzyme-phosphate complex and then release the phosphate group.