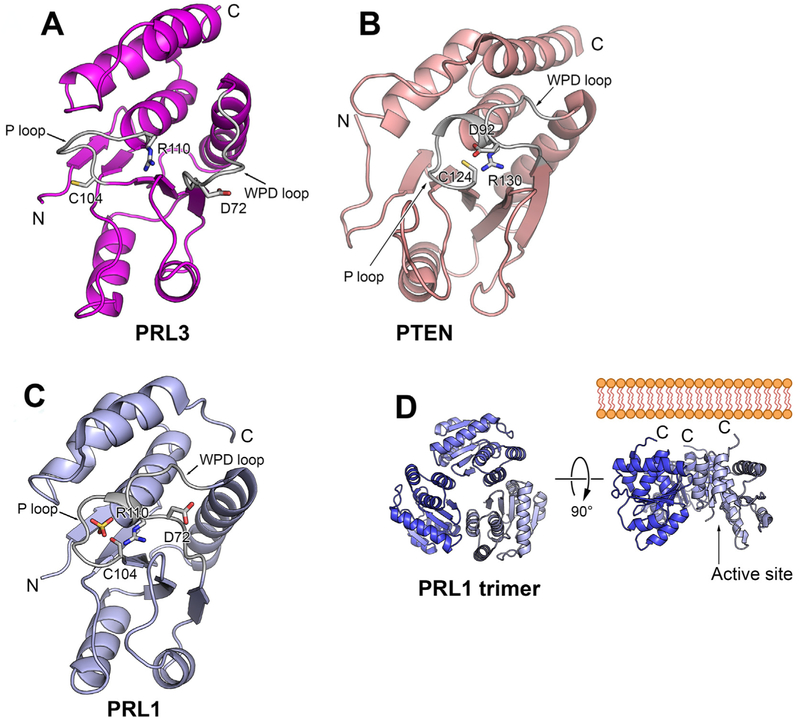
Fig. 3.
Comparison of PRLs structure and active site conformation. A) Cartoon view of PRL-1 monomer structure (Protein Data Bank code 1XM2) shows that PRL-1 adopts a closed conformation with the conservative aspartate residue (D72) in proximity to catalytic cysteine (C104). B) Cartoon view of PTEN reveals a close conformation in the active site (PDB ID 1D5R). The second domain of PTEN is omitted for clarity. C) Cartoon view of PRL-3 (Protein Data Bank code 1R6H) shows that PRL-3 adopts an open conformation with the conservative aspartate residue (D72) away from catalytic cysteine (C104). D) PRL exists as a trimer in the crystal (Protein Data Bank code 1XM2). Trimerization exposes C-terminal prenylation motif that anchors PRL-1 on the inner membrane. The active P-loop was located on the opposite side of the trimer.