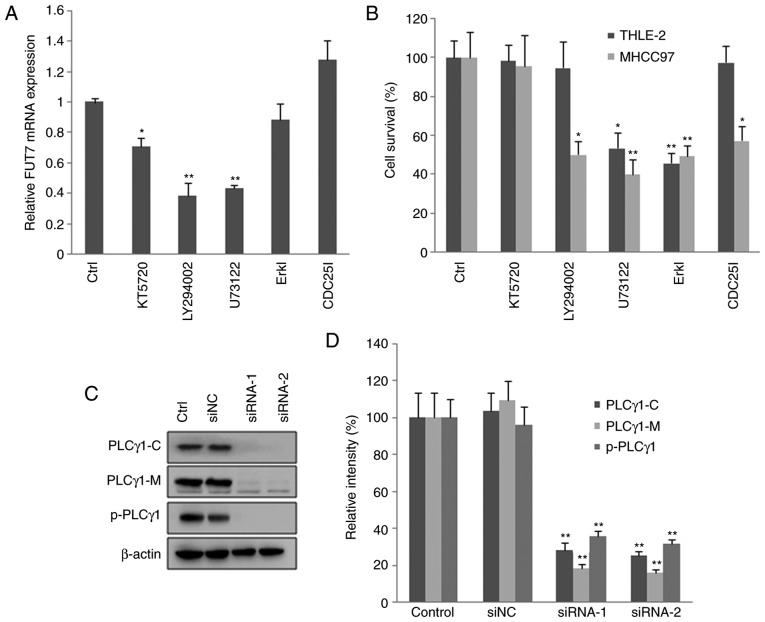
Figure 4.
Knocking down FUT7 affects cell survival via various intracellular signaling mediators. MHCC97 cells were transfected with FUT7 siRNAs. After 1 h, inhibitors of signaling molecules were added to the culture medium, and the cells were cultured for a further 48 h for RNA analysis and 72 h for protein analysis. (A) mRNA levels of FUT7 were quantified by reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction following treatment with inhibitors. (B) Following treatment with the inhibitors, cell survival was quantified using a 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H tetrazolium bromide assay in the THLE-2 normal liver cells and MHCC97 hepatocarcinoma cells. (C) Cells were permeabilized and centrifuged to isolate the cytosolic proteins and particulate-conjugated proteins. Results of western blot analysis of the target proteins are shown with profiles. (D) Quantitative analysis of relative protein levels. *P<0.05 (n=3), vs. Control; **P<0.01 (n=3), vs. Control. FUT, fucosyltransferase; Ctrl, control (no inhibitor); ErkI, extracellular signal-regulated kinase inhibitor; siRNA, small interfering RNA; siNC, scramble-siRNA transfected cells; PLCγ, phospholipase Cγ; PLCγ1-C, PLCγ1 in cytoplasm; PLCγ1-M, PLCγ1 conjugated with plasma membrane; p-PLCγ1, phosphorylated PLCγ1 conjugated with plasma membrane; Control, untransfected cells.