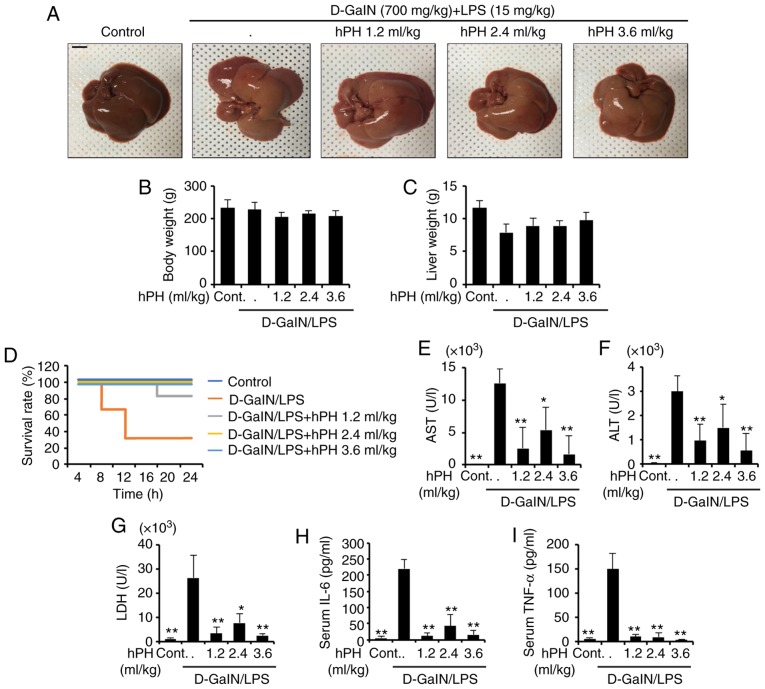
Figure 1.
Protective effects of hPH treatment on D-GalN/LPS-induced acute liver failure. hPH (1.2, 2.4, or 3.6 ml/kg) was subcutaneously administered to rats three times at intervals of 24 h, followed by exposure to 700 mg/kg D-GalN and 15 µg/kg LPS (D-GalN/LPS). Livers from each experimental group were examined 24 h following D-GalN/LPS challenge. (A) Gross image of livers. Scale bar=1 cm (B) Animal weights (n=4-6) were measured just prior to sacrifice; with no statistical difference among groups. (C) Liver weights were measured following sacrifice, with no statistical difference among groups (n=4-6). (D) Survival rates of rats were observed for 24 h following D-GalN/LPS exposure (n=12). Serum (n=4-6) was collected from animals 24 h following exposure to D-GalN/LPS to determine levels of (E) AST, (F) ALT, (G) LDH, (H) IL-6, and (I) TNF-α. All data are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01, vs. D-GalN/LPS group. hPH, human placental hydrolysate; D-GalN, D-galactosamine; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; Cont, control; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; IL-6, interleukin-6; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α.