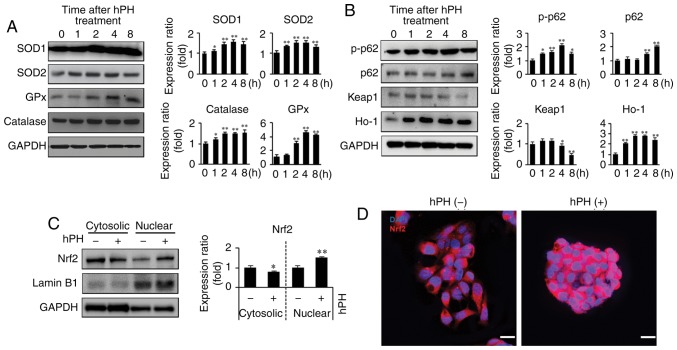
Figure 5.
Upregulation of antioxidant enzymes and regulation of Keap1-Nrf2 in hPH-treated HepG2 cells. (A) Lysates from hPH-induced HepG2 cells were immunoblotted with anti-SOD-1, anti-SOD-2, anti-GPx, or anti-catalase antibodies. Representative images (left penal), densitometry results (right panel). All data are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs. 0 h time point. (B) Following treatment with hPH, the expression levels of p-p62, p62, Keap1, and HO-1 were determined by western blot analysis. Representative images (left penal), densitometry results (right panel). All data are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, vs. 0 h time point. (C) Nuclear localization of Nrf2 in hPH-treated HepG2 cells compared with untreated HepG2 cells. Lysates from hPH-treated HepG2 cells were immunoblotted with anti-Nrf2, anti-Lamin B1, or anti-GAPDH antibodies. Representative images (left penal), densitometry results (right panel). All data are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, vs. 0 h time point. (D) HepG2 cells post-hPH treatment were immunostained with anti-Nrf2 antibody. Nuclei were identified using DAPI staining (scale bar=20 µm). hPH, human placental hydrolysate; SOD, superoxide dismutase; GPx, glutathione peroxidase; Keap1, Kelch-like ECH2-associated protein 1; HO-1, heme oxygenase-1; p-p62; Nrf2, nuclear factor-E2-related factor 2.