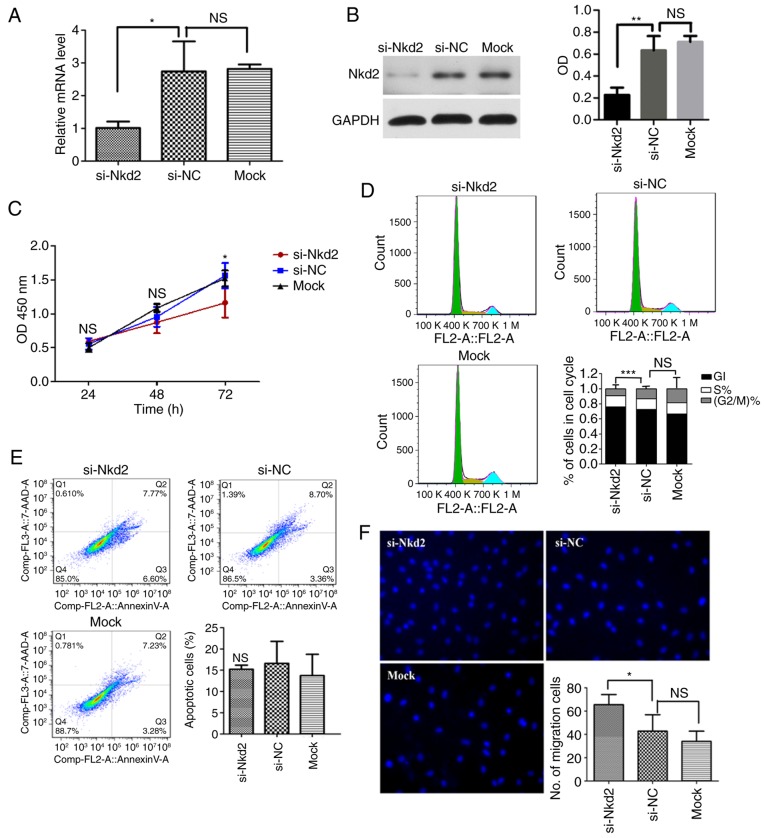
Figure 3.
Effect of si-Nkd2 transfection on rDFSCs. (A) Efficiency of si-Nkd2 transfection in rDFSCs determined by reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction. A total of 48 h after si-Nkd2 transfection, the levels of Nkd2 mRNA in the si-Nkd2 group were significantly lower compared with that in the si-NC group, but there was no difference between the si-NC and Mock groups. (B) Efficiency of si-Nkd2 transfection in rDFSCs determined by western blotting. A total of 72 h after si-Nkd2 transfection, the Nkd2 protein levels in the si-Nkd2 group were significantly lower compared with that in the si-NC group, but there was no difference between the si-NC and Mock groups. (C) Cell Counting Kit-8 assay results revealed that the proliferation of si-Nkd2-transfected rDFSCs was significantly lower compared with that of si-NC-transfected rDFSCs at 72 h after transient transfection. (D) A total of 72 h after transient transfection, cells were arrested in the G1 phase, and their rate of entry into G2 phase was diminished. (E) Silencing of Nkd2 had no significant effect on apoptosis rates in rDFSCs. (F) Transwell assay results demonstrated significantly increased migration in Nkd2-silenced rDFSCs. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01 with comparisons shown by lines. si-, small interfering RNA; Nkd2, naked cuticle homolog 2; NC, negative control; NS, not significant; OD, optical density; rDFSC, rat dental follicle stem/progenitor cell.