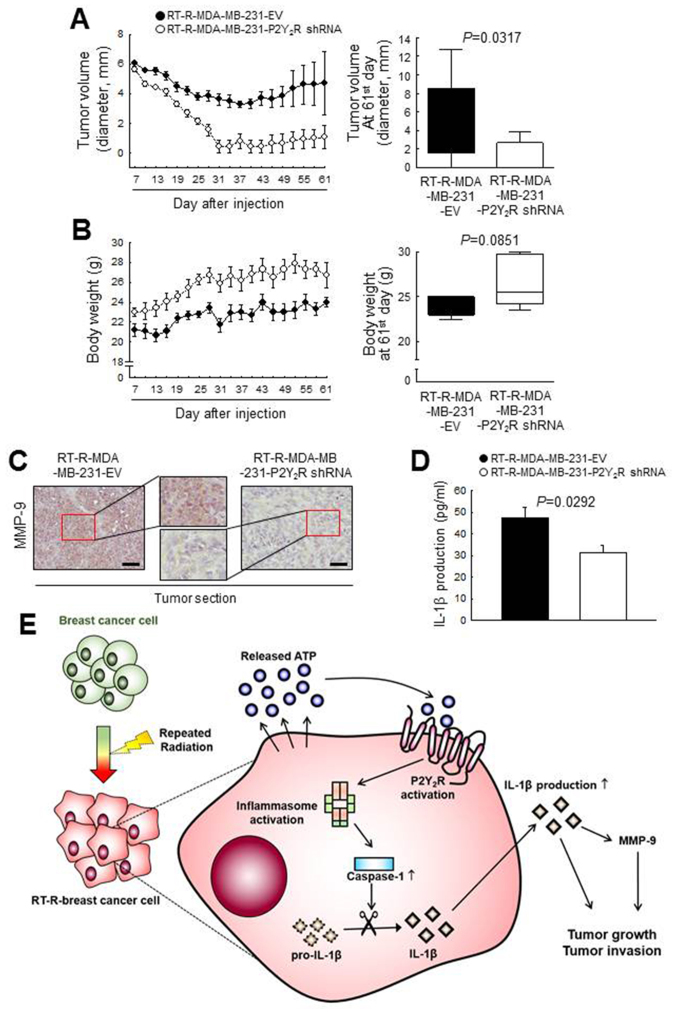
Figure 6.
Suppression of P2Y2R reduced RT-R-breast cancer cell growth by regulating MMP-9 expression in an in vivo mouse model. Athymic nude mice were divided into 2 groups and injected subcutaneously with empty vector-transfected RT-R-MDA-MB-231 cells (RT-R-MDA-MB-231-EV; n=5) or P2Y2R-shRNA- transfected RT-R-MDA-MB-231 cells (RT-R-MDA-MB-231-P2Y2R-shRNA; n=5) (5×106 cells/100 µl of serum-free medium). RT-R-MDA-MB-231-EV-injected or RT-R-MDA-MB-231-P2Y2R shRNA-injected animals were sacrificed on day 61. (A) Tumor volumes and (B) body weights were measured every 3 days during tumor development, and the bar graphs were presented at the end of 61st day. (C) Tumor tissue sections were stained with anti-MMP-9 antibody (scale bar, 100 µm), and the sections were counterstained with Mayer’s hematoxylin solution. (D) IL-1β levels in the serum were analyzed as described in the Materials and methods (n=3). (E) Schematic representation of the proposed role of P2Y2R in RT-R-breast cancer cell progression and invasiveness through interaction with the inflammasome.RT-R, radiotherapy-resistant; P2Y2R, P2Y purinergic receptor 2.