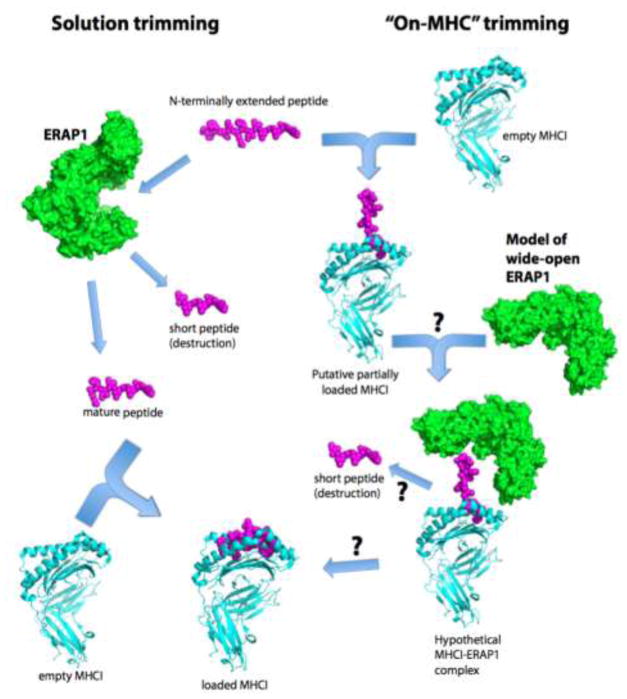
Figure 1.
Pathways for ERAP1-restricted peptide trimming. Left pathway, ERAP1 trims N-terminally extended peptides in solution down to mature, correct-length peptides that can then proceed to bind onto MHCI. Overtrimming to short peptides equates to epitope destruction. Right pathway, N-terminally extended peptides bind onto MHCI in a sub-optimal manner. Formation of a ternary complex with ERAP1 allows N-terminal trimming while the peptide is still bound on the MHCI. Optimal interactions between the generated mature epitope and the MHCI allow for ERAP1 dissociation.