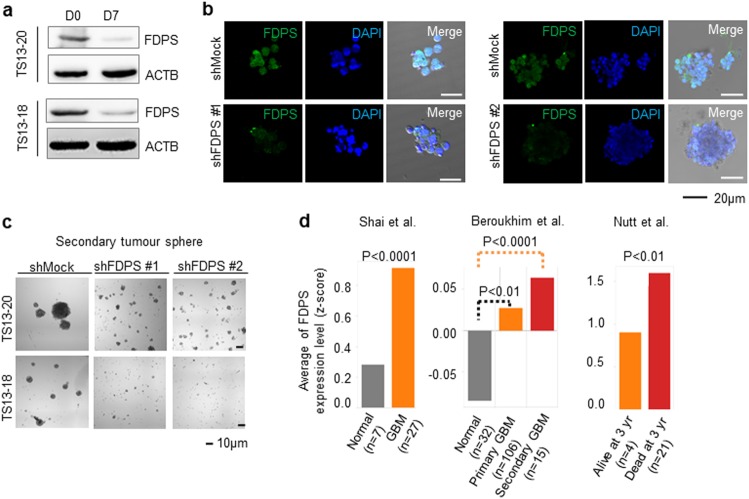
Fig. 4. Knockdown of farnesyl diphosphate synthase (FDPS) suppresses glioblastoma sphere formation.
a The protein levels of FDPS between TS13-20 and TS13-18 cell spheres (D0) and differentiated counterparts (D7) were analyzed by western blot. ACTB was used as the loading control. b TS13-20 cells were infected with lentivirus harboring short hairpin RNAs (shRNAs) against FDPS. Two days after infection, the infected cells were selected for 2 days and then maintained an additional 4 days. Knockdown of the FDPS protein was assessed by immunofluorescence staining and confocal microscopy. Images were obtained at ×20 using an LSM510 META or LSM780 confocal microscope (Carl Zeiss, Jena, Germany). c Knockdown of FDPS inhibited secondary sphere formation. The same number of control and FDPS knockdown cells were subjected to secondary sphere formation. Bright field images were obtained using a Cytation 3 microplate reader (Bio-Tek). d FDPS gene expression was significantly upregulated in glioblastoma cells compared with normal cells and in samples with a dead status at 3 years compared with samples with a live status. Three independent microarray-based data sets were median centered and normalized to the unit standard deviation to compare the gene expression level according to the P-value